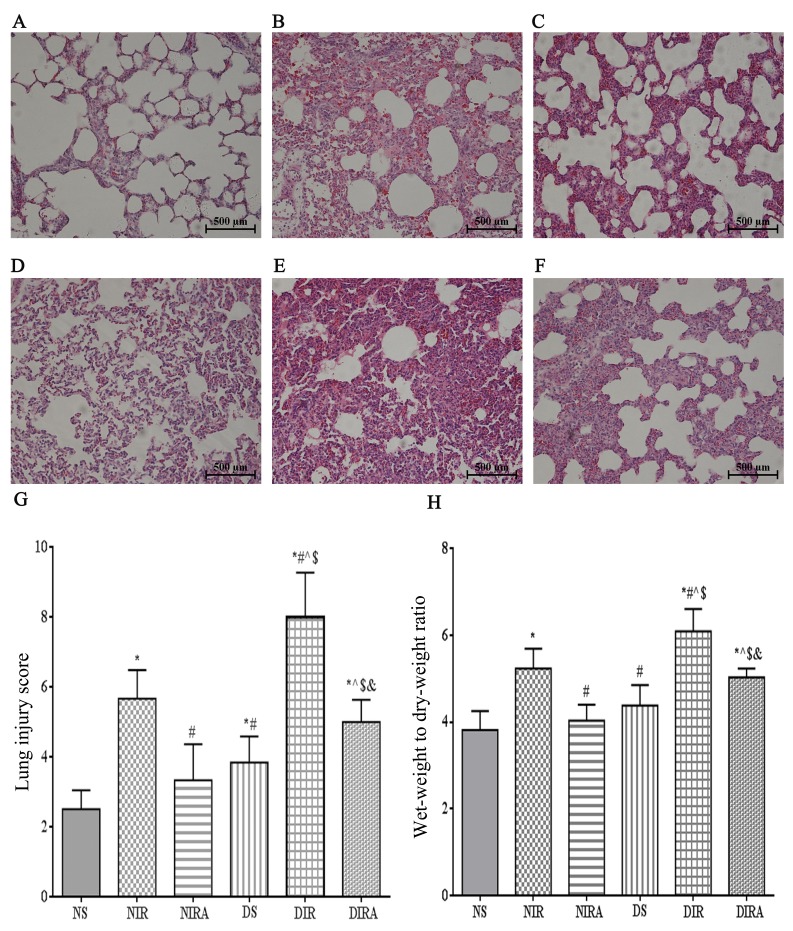
Figure 1.
Diabetes mellitus increases susceptibility to lung I/R injury. Adiponectin improved the IR-induced pathological alterations in lung tissue (hematoxylin and eosin staining, lung injury score, and wet-weight to dry-weight ratio). (A) NS, (B) NIR, (C) NIRA, (D) DS, (E) DIR and (F) DIRA groups. Scale bar=500 µM. (G) Lung injury score and (H) wet-weight to dry-weight ratio were determined. The results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05 vs. NS group, #P<0.05 vs. NIR group, ^P<0.05 vs. NIRA group, $P<0.05 vs. DS group and &P<0.05 vs. DIR group. DIR, diabetic I/R group, in which the lung was subjected to 90 min of ischemia and 4 h of reperfusion; DIRA, diabetic I/R + gAPN group, in which 10 µg gAPN was injected 10 min prior reperfusion; DS, diabetic sham group, in which the left lung hilum was not clamped; NIR, I/R, in which the lung was subjected to 90 min of ischemia and 4 h of reperfusion; NIRA, I/R + gAPN, in which 10 µg gAPN was injected 10 min prior to reperfusion; NS, Sham group, in which the left lung hilum was not clamped. I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; gAPN, adiponectin globular domain.