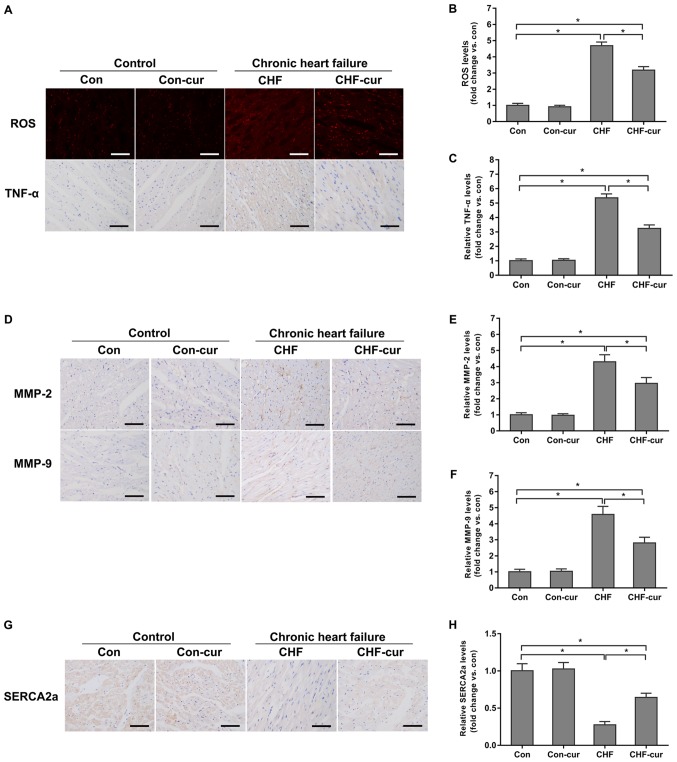
Figure 2.
Effects of curcumin on the expression of CHF molecular biomarkers. (A) Representative images of ROS and TNF-α staining and quantification of (B) ROS and of (C) TNF-α expression levels, as measured by DHE (ROS) and immunohistochemical staining (TNF-α) in LVAW cardiomyocytes. (D) Representative images of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and quantification of (E) MMP-2 and (F) MMP-9 expression levels, as measured by immunohistochemical staining in LVAW cardiomyocytes. (G) Representative images of SERCA2a and (H) quantification of its expression levels, as measured by immunohistochemical staining in LVAW cardiomyocytes. Magnification, ×200. Scale bar=50 µm. All data are expressed as the mean ± stadard deviation, n=10. *P<0.05. CHF, chronic heart failure; Con, control; Cur, curcumin; LVAW, left ventricular posterior wall thickness; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SERCA, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase; TNF, Tumor necrosis factor; DHE, dihydroethidium.