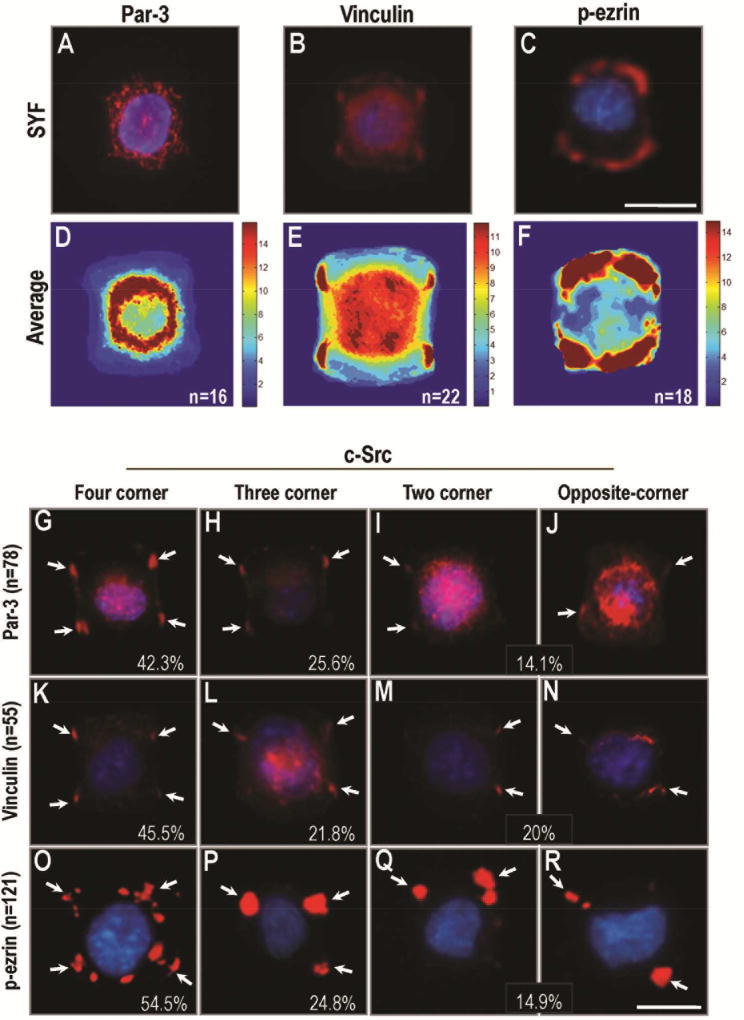
Figure 4. Src controls the distribution of cortical cues on the cell cortex.
(A–C) Expression of proteins associated with cortical actin activity in SYF cells after plating on I-type micropattern. Par-3 was expressed uniformly in the cytoplasm of SYF cells (A). Vinculin was distributed at the sites of cell attachment to ECM in almost all SYF cells (B). Expression of p-ezrin was preferentially localized at the sites of cell-matrix attachment in SYF cells (C).
(D–F) The average distribution of Par-3, Vinculin and p-ezrin was shown in D, E, F.
(G–R) Src re-expression contributed to the diverse distribution of Par-3 (G–J), Vinculin (K–N), and p-ezrin (O–R) at the sites of cell-matrix adhesion in c-Src overexpressing cells. (G–J) The expression of Par-3 in c-Src over-expressing cells after plating on I-type micropattern (42.3% in four-corner attachment, 25.6% in three-corner attachment, and 14.1% in two-corner attachment). (K-N) The expression of Vinculin in c-Src over-expressing cells after plating on I-type micropattern (45.5% in four-corner attachment, 21.8% in three-corner attachment, and 20% in two-corner attachment). (O–R) The expression of ezrin in c-Src over-expressing cells after plating on I-type micropattern (54.5% in four-corner attachment, 24.8% in three-corner attachment, and 14.9% in two-corner attachment). Scale bars represent 20µm. All results are representative of 3 independent experiments.