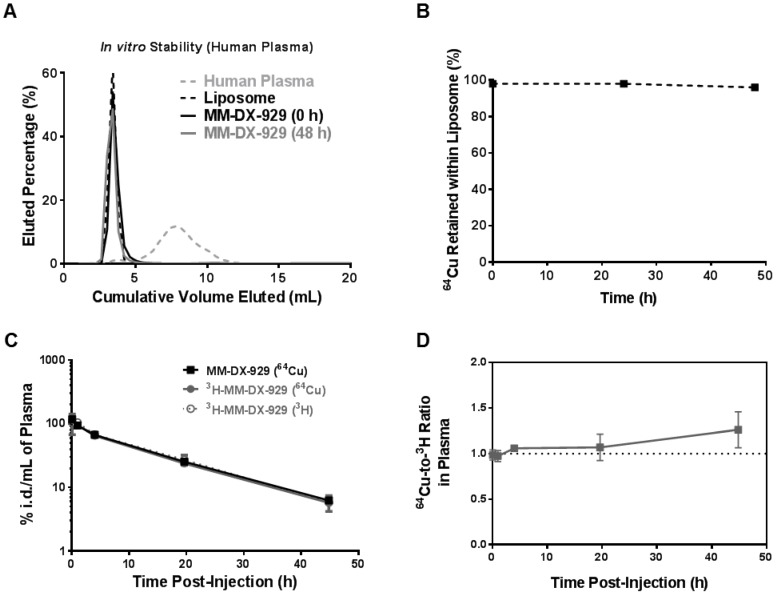
Figure 2.
In vivo and in vitro stability of 64Cu encapsulation in MM-DX-929. (A) Sepharose CL4B columns were characterized using fluorescently-labeled liposome or human plasma to determine the fractions at which liposome-bound or plasma-protein-bound 64Cu:4-DEAP-ATSC elute, respectively. Free 64Cu is retained within the column with < 3% of recovery from elution at 100 mL of cumulative volume. Following incubation with human plasma at 37ºC for 0 h and 48 h, aliquots of MM-DX-929/plasma mixture were loaded onto the columns to separate the liposomal 64Cu from non-liposomal 64Cu. (B) The percentage of 64Cu retained within the liposome was determined from (A) by dividing the 64Cu signal recovered from MM-DX-929 in the liposome fraction by the total radioactivity recovered. (C) Mice were injected with a single dose of MM-DX-929 or 3H-MM-DX-929. At designated time points up to 48 h.p.i., a blood sample was collected via saphenous vein puncture. 64Cu and 3H radioactivity in the plasma fraction was quantified using scintillation-counting. Data is decay-corrected. 3H serves as a stable tracer for the liposomal component of MM-DX-929 and was incorporated into the formulation as 3H-CDHE. (D) Ratio of 64Cu-to-3H in plasma derived from (C) was plotted as a function of time post-injection.