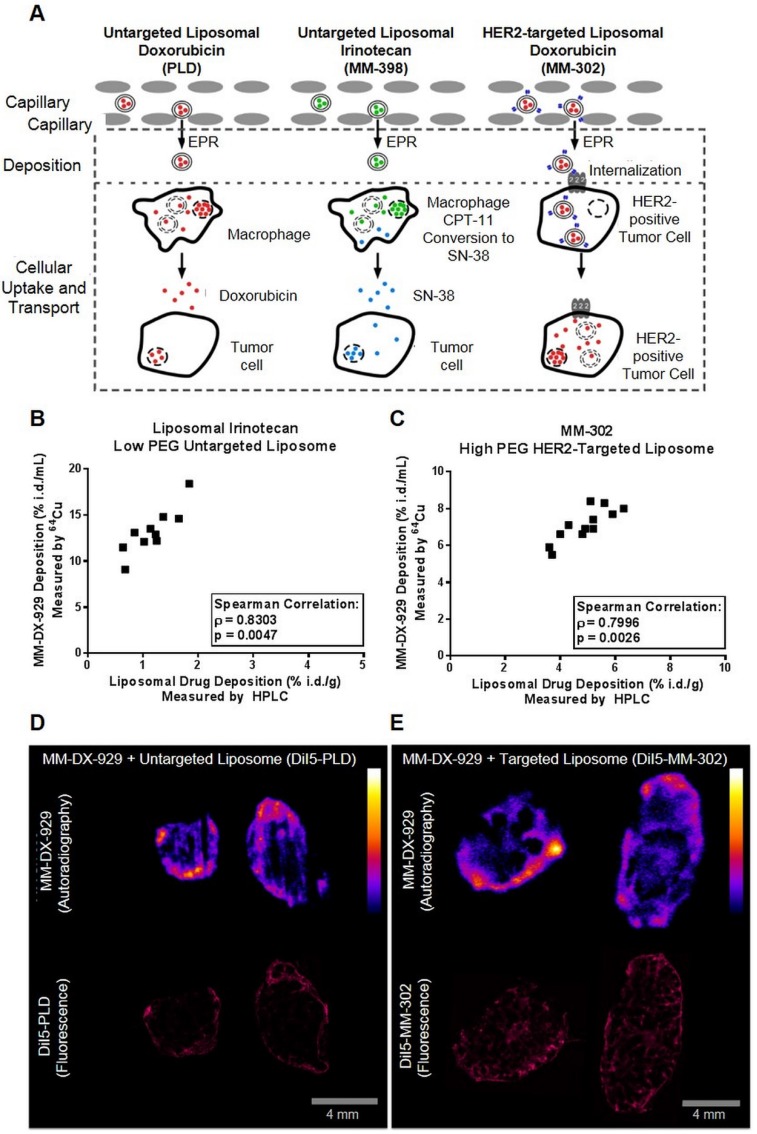
Figure 5.
Correlation of MM-DX-929 tumor deposition and intratumoral distribution with liposomal drugs. (A) Schematic depicting the mechanism in which liposomal drugs are delivered from circulation into the cellular target. Liposome deposition and transport into tumors from circulation via the EPR effect is a shared step for liposomal drugs with different physico-chemical properties. The intratumoral fate of the liposome and drug payload is determined after the deposition step depending on the design of the liposomal drug system. Mice bearing (B) HT-29 subcutaneous tumors and (C) BT474-M3 orthotopic mammary fat pad tumors were co-injected with MM-DX-929 and liposomal irinotecan (10 mg/kg) or MM-302 (3 mg/kg), respectively. At 24 h.p.i., mice were perfused with PBS and tumors were excised for quantification of 64Cu and drug content. Mice bearing BT474-M3 tumors were co-injected with MM-DX-929 and (D) DiI5-PLD (3 mg/kg) or (E) DiI5-MM-302 (3 mg/kg), respectively. Autoradiography was performed to obtain intratumoral distribution of MM-DX-929 at 24 h.p.i.; consecutive sections were used to obtain intratumoral distribution of DiI5-PLD or DiI5-MM-302 using Aperio ScanScope.