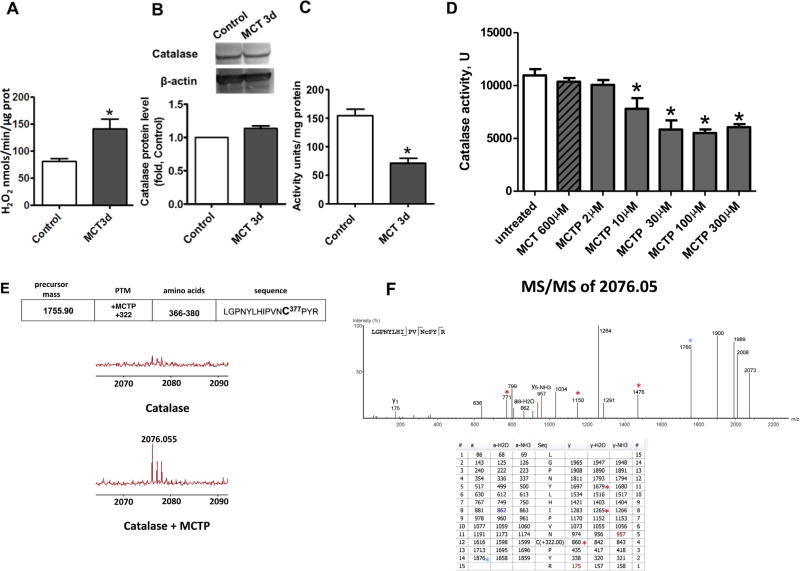
Fig. 1.
Monocrotaline pyrrole inhibits catalase activity through adduct formation at cysteine 377. The level of H2O2 produced in snap frozen peripheral lung tissue is increased 3 days after MCT injection (A). Despite no changes in catalase protein as determined by Western blot analysis and normalized to β-actin (B), catalase activity is significantly attenuated in MCT-treated rats. MCTP, but not MCT, attenuates recombinant human catalase (D) and this corresponds to the addition of the pyrole adduct to cysteine 377 located in the peptide sequence 366-LGPNYLHIPVNC*PYR-380 as determined by MS (E). MS/MS spectra (F, upper panel) were analyzed with PEAKS 5.2 software and the resulting ion table is shown (F, lower panel). Due to instability of MCTP modification, the fragmentation was calculated manually. Colored numbers represent predicted y,b ions in MS/MS with MCTP attached to cysteine 377 and colored *-symbols indicate predicted collision products with fragmented MCTP modification. Results are expressed as mean±SEM; n=3–8. *P<0.05 vs. control or untreated group.