Fig. 7.
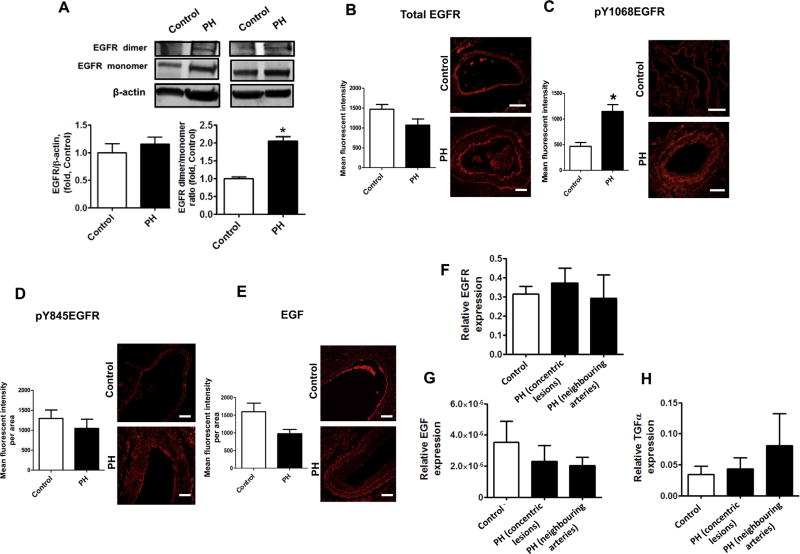
Ligand independent EGFR activation in pulmonary arteries of patients with advanced pulmonary hypertension. The levels of total EGFR in human peripheral pulmonary tissue were measured by Western blot analysis and normalized on the level of β-actin. There was no significant difference between total EGFR levels in controls and patients with advanced PH (A, left panel). Two representative sets are shown The levels of SDS-resistant EGFR dimer were also evaluated by performing Western blot analysis. Due to differences in expression levels, two different exposure times were used for each blot to measure EGFR monomers and EGFR dimers. Thus, each box represents the same gel but different exposure times. The levels of SDS-resistant EGFR dimer (A, right panel) was significantly increased in lung tissues patients with advanced PH. Immunofluorescence was performed on paraffin tissue sections using antibodies against EGFR (B), pY1068EGFR (C), pY845EGFR (D) and EGF (E) followed by an Alexa Fluor® 546 secondary antibody. Pulmonary artery walls of controls and patients with PH were traced to obtain mean fluorescent signal per area (n=60 pulmonary arteries). Representative images are shown. The fluorescent signal for EGFR (B), pY845EGFR (D) and EGF (E) were not different between controls and patients with advanced PH. However, EGFR auto-phosphorylation (pY1068EGFR) was significantly increased in the pulmonary artery wall of patients with advanced PH (C). Messenger RNA levels were also measured using laser-assisted microdissection followed by qRT-PCR in pulmonary arteries of control and concentric lesions and neighboring arteries in patients with advanced PH. EGFR (F) and EGF (G) and TGFα (H) mRNA levels were not different between controls and patients with advanced PH. Results are expressed as mean±SEM; N=3–17. *P<0.05 vs. controls. Scale bars are equal to 200 µm.