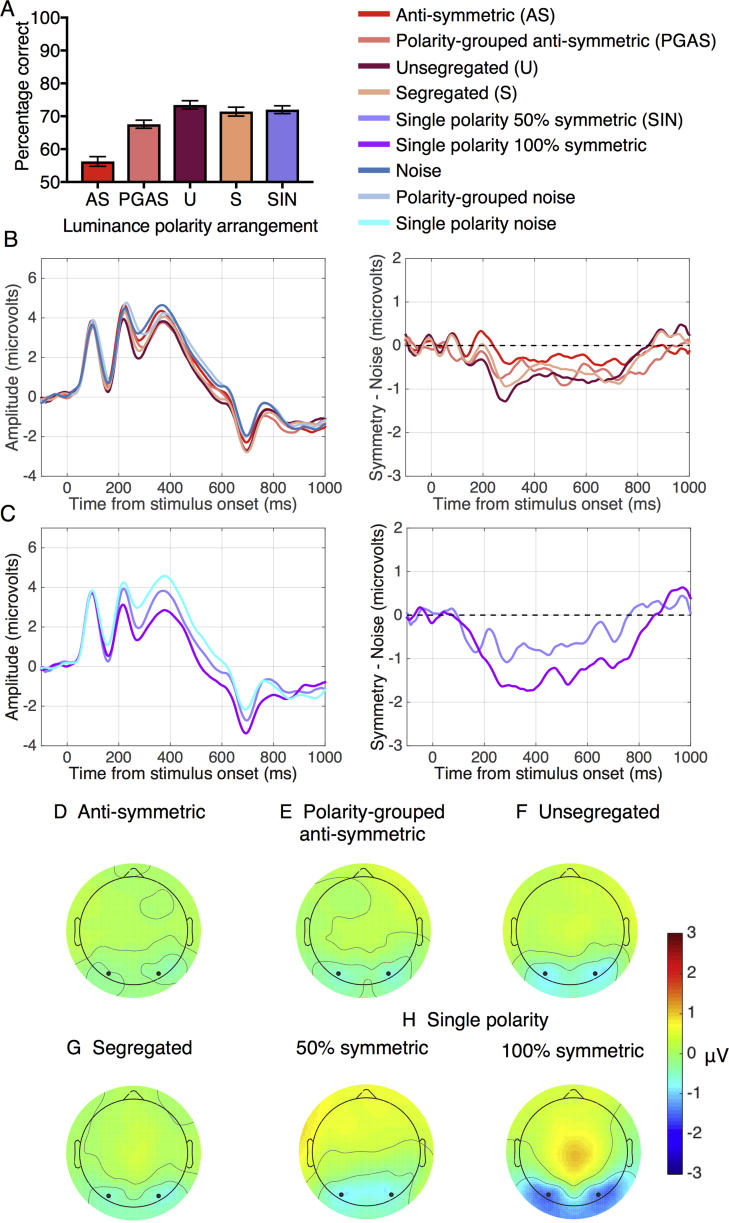
Fig. 5.
Results for Experiment 2. (A) Performance (% correct answers) in the symmetry detection task with segregated, unsegregated, anti-symmetric, polarity-grouped anti-symmetric and single polarity patterns containing 50% position symmetry. (B) Grand-average ERPs (left) and SPN (right) difference wave for anti-symmetric, polarity-grouped anti-symmetric, segregated and unsegregated patterns; (C) Grand-average ERPs (left) and the SPN difference wave for single-polarity patterns containing 50% and 100% position symmetry. Waveforms depict the average of electrodes PO7 and PO8. (D–H) Topographic difference map for anti-symmetric (D), polarity-grouped anti-symmetric (E), unsegregated (F), segregated (G) and single polarity patterns containing 50% and 100% position symmetry (H). Each topographic difference map shows the difference between symmetry and noise in the 200–600 ms time window. Black dots indicate the position of electrodes PO7 and PO8.