Figure 1. p205 is induced by LPS, Type I and II IFN and localizes to the nucleus.
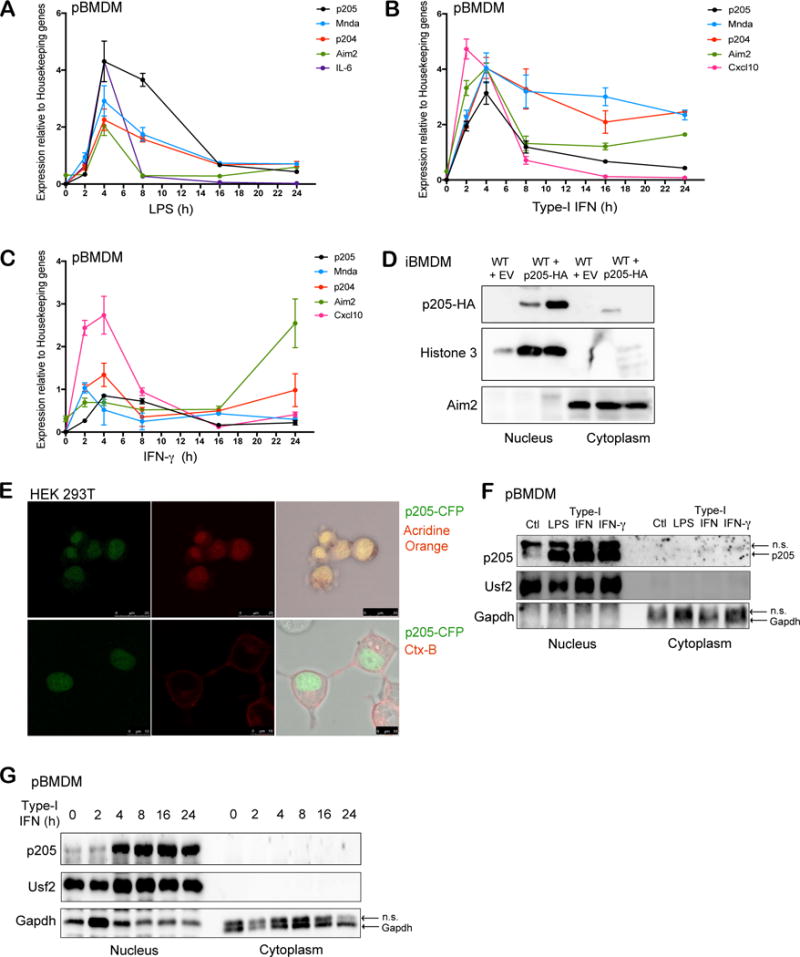
Primary BMDMs stimulated with (A) LPS (200 ng/ml), (B) Type-I IFN (100 U/ml) or (C) IFN-γ (20 ng/ml) at different time points (0, 2, 4, 8, 16, 24 h) were tested for p205 mRNA expression as well as other PYHIN genes, Mnda, p204 and Aim2. Levels of IL-6 or Cxcl10 mRNA were included as positive controls. Gene expression is reported relative to a combination of three housekeeping genes Gapdh, Hprt, β-actin. (D) Immunoblot analysis of the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of wild-type BMDM transduced with empty vector (EV) and wild-type BMDM overexpressing HA-tagged p205 using anti-HA antibody. Histone 3 and Aim2 were used as controls for nuclear and cytosolic extracts respectively. (E) Confocal microscopy of CFP-tagged p205 (green) in HEK 293T cells stained for nucleus using Acridine orange in first panel and Cholera Toxin B (CtxB) staining plasma membrane in second panel. Data is representative of two independent experiments. (F) Primary BMDM untreated (Ctl) or treated with LPS for 6h, type-I IFN for 16h or IFN-γ for 16h were separated into nuclear and cytosolic fractions and immunoblotted for endogenous p205 (n.s.- non-specific band). (G) Western blot analysis of endogenous p205 expression in the nuclear and cytosolic extracts of primary macrophages treated with type-I IFN as indicated. Usf2 and Gapdh were used as controls for nuclear and cytosolic fractions respectively (n.s.- non-specific band).
