FIGURE 2.
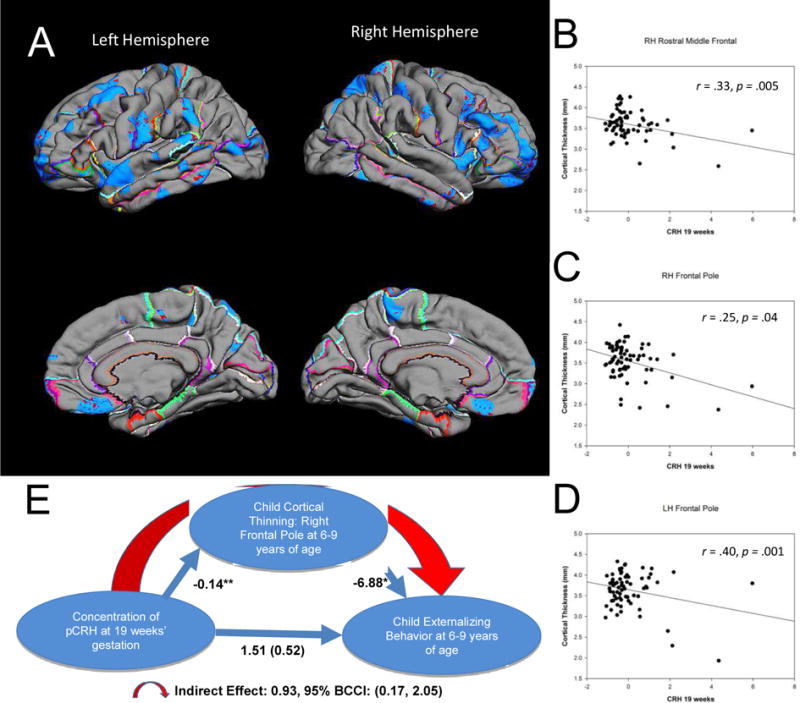
Pial maps (A) illustrating statistically significant areas of cortical thinning associated with prenatal levels of pCRH at 19 weeks gestation. Representative scatterplots (B [r=.33, p=.005] C [r=.25, p=.04], D [r=.40, p=.001]) of the significant associations between pCRH and cortical thinning in cortical subregions. Model (E) of the indirect significant association among prenatal concentrations of pCRH, child cortical thinning in the frontal pole and child internalizing behavior. The values correponding to each path in the model are unstandardized regression coefficients. The indirect effect was estimated with bootstrapping (1000 samples with replacement).
