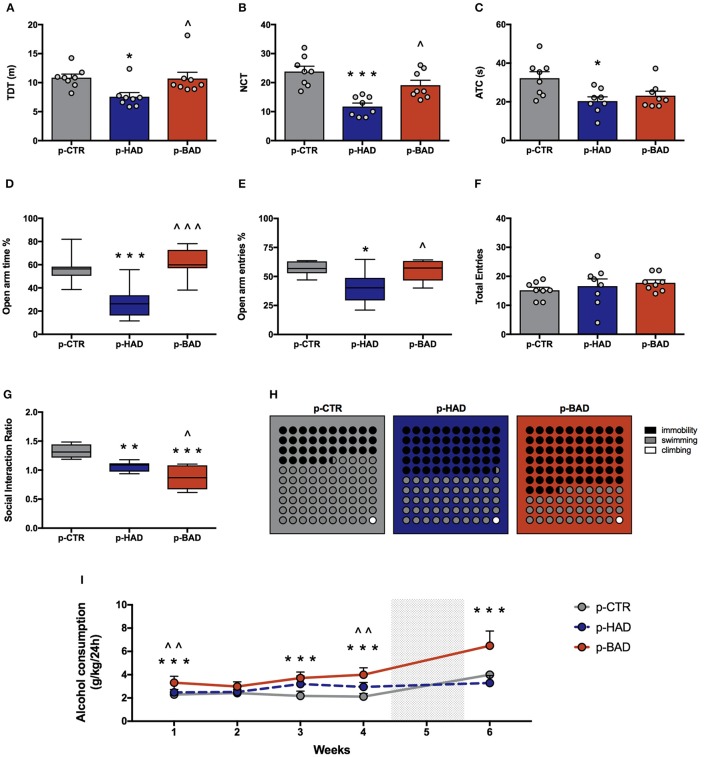
Figure 4.
Offspring phenotype and alcohol vulnerability. Pre-and post-gestational habitual (p-HAD) and binge (p-BAD) alcohol drinking affect offspring behavioral reactivity, anxiety-like behavior, social reward sensitivity, and depression-like behavior. Open field test—(A) total distance traveled (TDT); (B) number of transitions in central areas (NTC); and (C) amount of time spent on the central areas of the arena (ATC). Elevated plus maze test—(D) percentage of time spent on the open arm; (E) percentage of entries in the open arm; (F) total entries. (G) Social interaction test; (H) Forced swim test, where the parts-of-whole−10 × 10 dot—plots represent normalized mean values from immobility time (black); swimming time (gray); climbing time (white) in the three experimental groups. (I) Vulnerability to alcohol abuse is measured in the two bottle choice paradigm during drinking induction (weeks 1–4) and relapse following forced abstinence (week 6). Each bar and each dot represents the mean ± SEM of n = 8 rats. Each box-and-whisker plot represents the median (horizontal line in the box), 25–75% (box) and min-to-max (whiskers) values of n = 8 rats. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs. p-CTR rats; ∧p < 0.05; ∧∧p < 0.01; ∧∧∧p < 0.001 vs. p-HAD rats.