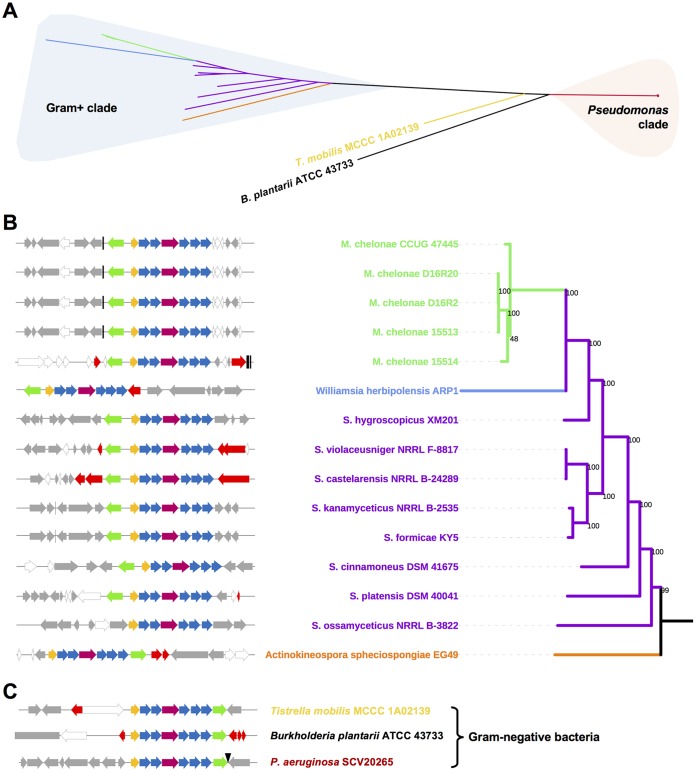
FIG 4.
Phylogeny and genetic context of the bcm gene clusters. (A) Unrooted maximum likelihood tree of the nucleotide sequences from the bcm gene clusters identified in this work. Branches are color-coded by genus, and major clades are highlighted. (B) Detailed view of the phylogeny and genetic context of the bcm clusters in Gram-positive bacteria. Bootstrap support values for the phylogeny are shown at the base of each branch, and the genetic context of each cluster (color-coded as in Fig. 1B) is shown for each branch of the tree. Flanking genes are color-coded gray if they encode proteins with conserved domains, white for hypothetical proteins with no conserved domains, and red for proteins related to mobile genetic elements (see Table S5 for details). Vertical black lines represent tRNA genes. (C) Genetic context of the bcm clusters in Gram-negative bacteria. The black triangle represents an attTn7 site.