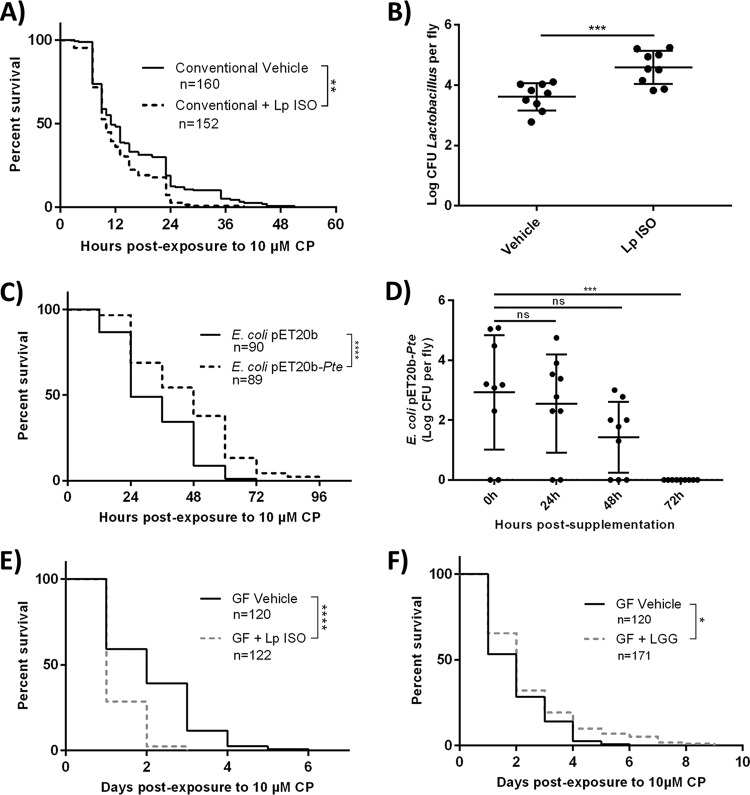
FIG 4.
Excess L. plantarum ISO increases toxicity of CP while probiotic L. rhamnosus GG and E. coli(pET20b-Pte) decrease toxicity to CP. (A) Survival curves of newly eclosed flies exposed to 10 μM CP with or without concurrent supplementation of L. plantarum ISO. (B) Surface-sterilized flies were homogenized and drop plated on MRS agar, and bacterial CFU per fly were enumerated after 48-h anaerobic incubations. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations (unpaired, two-tailed t test) from at least 3 independent experiments (each dot represents 10 individuals normalized to CFU per fly). (C and D) E. coli(pET20b-Pte) or vehicle E. coli(pET20b) was supplemented to D. melanogaster adults on normal food for 48 h, followed by the assessment of survival on 10 μM CP-spiked medium (C) or the enumeration of gut bacterial loads following transfer to fresh food (D). (E and F) Germfree (GF) flies were exposed to 10 μM CP with or without concurrent supplementation with L. plantarum ISO (E) or L. rhamnosus GG (F) and subsequent survival was recorded. Data represent at least 3 independent experiments. Statistical analyses shown for all survival curves are from log rank (Mantel-Cox) tests. ****, P < 0.0001; ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01, *, P < 0.05.