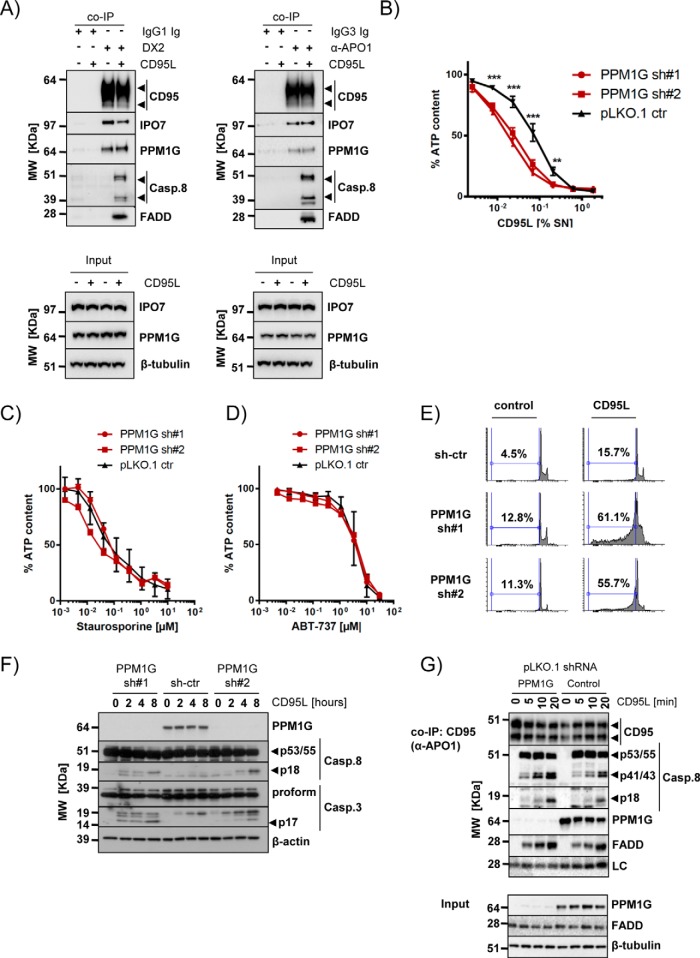
Fig. 7.
Validation of IPO7 and PPM1G interaction with CD95/FAS and PPM1G function. A, Copurification of PPM1G and IPO7 with CD95/FAS using two different anti-CD95/FAS antibodies (DX2 and α-APO1) under native expression conditions (arrowheads: specific signals). B, PPM1G knockdown sensitizes cells to CD95/FAS-induced cell death. BJAB cells were knocked down with two independent PPM1G shRNAs and treated for 24 h with a CD95L as indicated. Viability was determined by cell titer glo assay. Shown are average and S.D. of eight independent experiments (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ANOVA). C–D, PPM1G knockdown does not sensitize BJAB cells for Staurosporine (C) or ABT-737 (D). BJAB cells were knocked down as in (B) and treated for 24 h with the indicated drugs at different dilutions. Viability was determined by cell titer glo assay. Shown are average and S.D. of four independent biological experiments. E, DNA fragmentation of BJAB cells silenced for PPM1G expression was analyzed by flow cytometry 16 h after CD95L addition. F, The processing of caspases upon CD95L stimulation of the cells described in (E) was investigated. Shown is a representative Western blot analysis for the indicated proteins (arrowheads: specific signals). G, Analysis of the CD95/FAS-DISC formed by 2 × 107 BJAB cells transduced with control or PPM1G shRNAs. The cells were stimulated with CD95L for the indicated timeframes and CD95/FAS was precipitated using α-APO1 ab and shown is a representative Western blot analysis for the indicated proteins. The total lysate is shown in the lower part (LC: mouse IgG light chain; arrowheads: specific signals).