Fig. 1. Scheme and principle of the experiment.
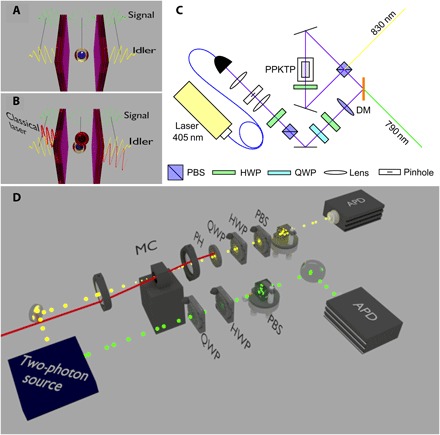
(A) Linear regime: A single photon (yellow, idler) gets into the microcavity, where it becomes a polariton, which is later reconverted into an external photon. When this photon is entangled with another (green, signal), we show that the entanglement is preserved throughout. (B) Interacting regime: A single photon (yellow, idler) enters the microcavity along with photons from a classical laser (red). The polaritons in the microcavity interact. This affects the entanglement of the single polariton in a way that allows measurement of the polariton-polariton interaction. (C) Sketch of the Sagnac interferometric source. DM, dichronic mirror. (D) Sketch of the setup implementing these configurations. PH, pinhole.
