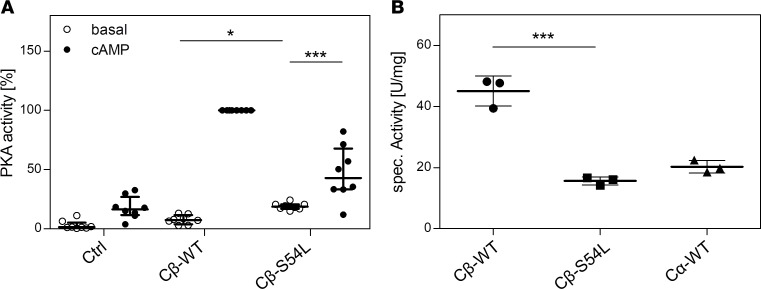
Figure 5. The mutation S54L causes increased phosphotransferase activity under basal conditions.
PKA activity was determined by quantifying the phosphorylation of a synthetic fluorescently labeled peptide (kemptide) in HEK293 cell lysates (A) or with unlabeled kemptide for purified recombinant catalytic subunits (B). In detail, (A) PKA activity was tested in lysates of HEK293 cells cotransfected with a combination of RIα and either WT or S54L Cβ1. Under basal conditions (no cAMP stimulation), the mutant holoenzyme showed higher PKA activity than the WT. In the presence of cAMP, maximal activity was lower for the mutant enzyme. Transfection of the empty pcDNA vector was used as control (Ctrl). Data from 4 independent experiments are represented as dot plots and were analyzed by ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. (B) PKA activity of purified recombinant RIα and catalytic subunits (Cβ-WT, Cβ-S54L, and Cα-WT) revealed an almost 3-fold-reduced phosphotransferase activity (15.6 ± 1.3 U/mg) for Cβ-S54L compared with Cβ-WT (45.1 ± 4.9 U/mg). The specific activity of the major isoform Cα1 was determined as a control (20.3 ± 2.0 U/mg). Data from 3 independent protein preparations are represented as dot plots and were analyzed by unpaired t test with Sidak’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.