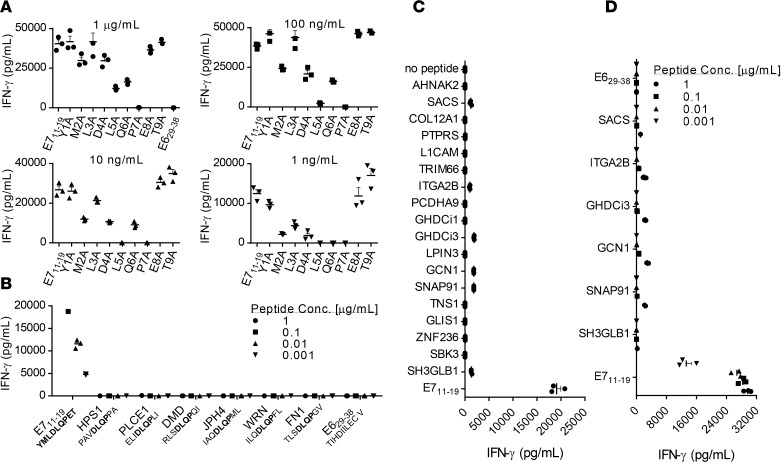
Figure 3. Testing of E7 TCR T cells for cross-reactivity against human peptides.
The assays shown were performed by coculture of E7 TCR T cells with T2 cells pulsed with the peptide indicated on the x axis. Coculture supernatants were harvested after 18–24 hours, and the IFN-γ concentration was measured by ELISA. Error bars represent the SEM of 3 technical replicates. (A) To guide cross-reactivity testing, alanine scanning of the E711–19 epitope was performed. An alanine residue was substituted for the native residue at each position of the E711–19 (YMLDLQPET) peptide. The residue substitutions are shown on the x axis. The peptide concentration is indicated above each bar graph. (B) Based on the findings in A, the amino acids at positions 4–7 (DLQP) were determined to primarily mediate E7 TCR recognition of E711–19. Position 2 also affected recognition, presumably due to its role as an HLA-A*02:01 anchor. A BLAST search was conducted to identify human peptides that share these 4 amino acids at the same positions and an HLA-A*02:01 anchor residue at positions 2 (L, M, T, or A) and 9 (V, I, L, T, or A) (48). E7 TCR T cells were tested for reactivity against T2 cells loaded with each of these peptides at the concentration indicated. (C) E7 TCR T cells were tested for recognition of a panel of human peptides that share either 6 residues or 5 residues plus a conservative substitution with E711–19. Target cells were loaded with 1 μg/ml peptide. (D) E7 TCR T cells were retested for reactivity against peptides identified as possibly reactive in C. The peptide concentrations are indicated.