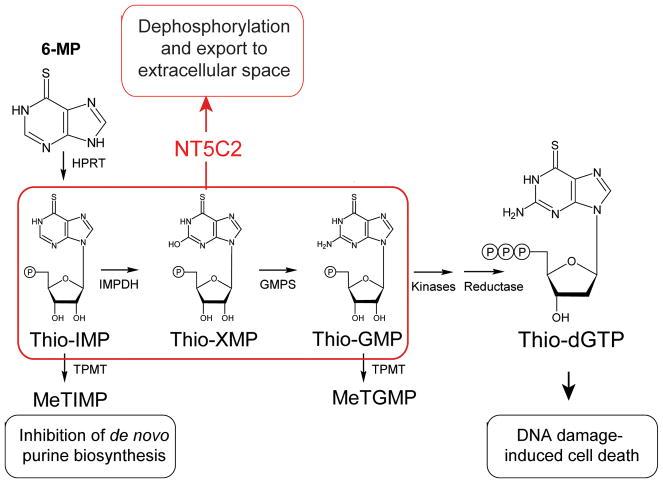
Extended Data Figure 1. Schematic representation of 6-MP activation and mechanism of action.
The hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase enzyme (HPRT) processes 6-MP to thio-IMP, which is then converted to thio-XMP and thio-GMP. Subsequent metabolism of thio-GMP by kinases and reductases yields thio-dGTP which is incorporated into replicating DNA strands and triggers the DNA mismatch-repair machinery, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. The anti-leukemic effects of 6-MP are in part also attributed to a second metabolic pathway whereby thiopurine S-methyl transferase (TPMT) methylates thio-IMP to form methylthio-IMP (MeTIMP), which is a potent inhibitor of amidophosphoribosyltransferase (ATase), an enzyme catalyzing the committed step of de novo purine biosynthesis.