Fig. 6.
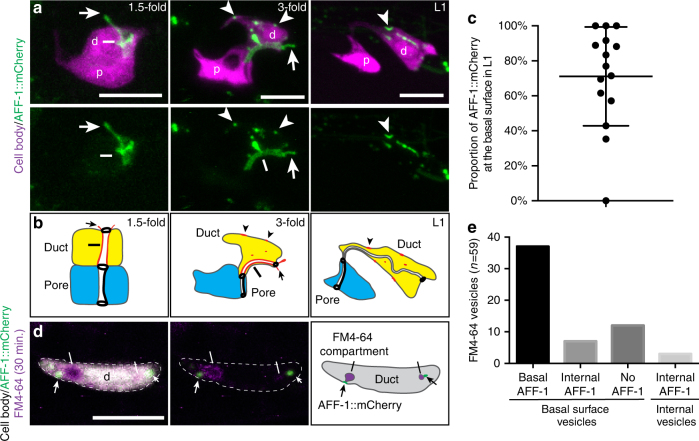
AFF-1 localizes to sites of auto-fusion and basal endocytosis. a Confocal Z-projections at different developmental stages in wild-type, d, duct; p, pore. The excretory duct and pore cell bodies are labeled with grl-2pro::YFP (magenta) and AFF-1 localization visualized with aff-1pro::aff-1::mCherry (green). At the time of duct auto-fusion, in 1.5-fold stage animals, AFF-1::mCherry localizes predominantly at the apical surface of the duct cell (line). The signal also extends dorsally (arrow); since the duct is the only aff-1 expressing cell in this region at this stage (Fig. 1e), the extension presumably corresponds to an extension of the duct apical domain into a neighboring cell such as the excretory canal tube or excretory gland, with which the duct lumen connects31. The localization of AFF-1::mCherry progressively shifts to become cytoplasmic and basal (arrowheads) in later stages. In L1 stage, AFF-1::mCherry is still present >6 h after duct auto-fusion. b Schematic interpretation. c Volocity quantification of the proportion of AFF-1::mCherry at the basal membrane in L1 larvae. Error bars = ± SD. d Confocal single slice of a wild-type L1 larva. AFF-1::mCherry (green) localizes adjacent to FM4-64-marked endocytosing vesicles (magenta and white bar) at the basal membrane of the duct cell (gray). e Quantification of the four categories of FM4-64 positive vesicles. Scale bar = 5 μm