Figure 6.
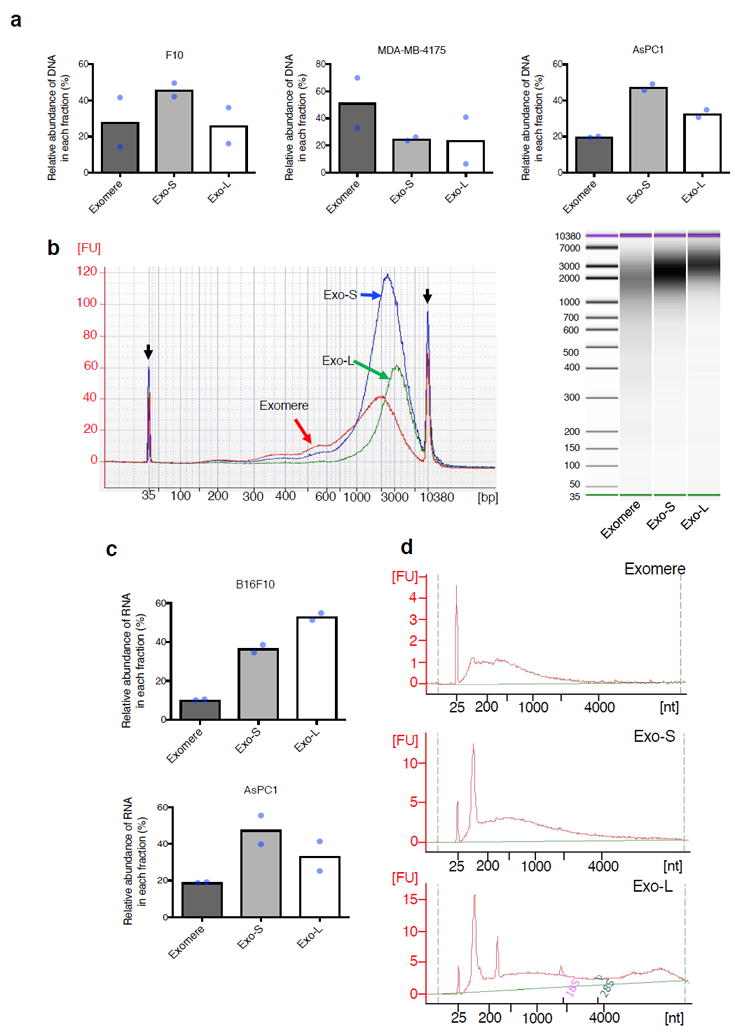
Characterization of nucleic acid association with exomere and exosome subsets. (a) Relative abundance of DNA associated with each subpopulation of particles from representative fractionations of B16F10, AsPC1 and MDA-MB-4175. (b) Agilent Bioanalyzer analysis of the size distribution of DNA associated with different subsets of particles. Data shown are the electropherograms (left) and electrophoresis images (right) from a representative of two independent experiments on AsPC1-derived particles. Black arrows, internal standards (35bp and 10380bp). Red line, exomeres; blue line, Exo-S; green line, Exo-L. (c) Relative abundance of total RNA associated with each subpopulation of particles from representative fractionations of B16F10 and AsPC1. (d) Size distribution of RNA isolated from different fractions of B16F10. Shown are representative profiles from one of two independent experiments. For (a) and (c), data shown are mean (n=2 biologically independent samples). Statistical source data are provided in Supplementary Table 8.
