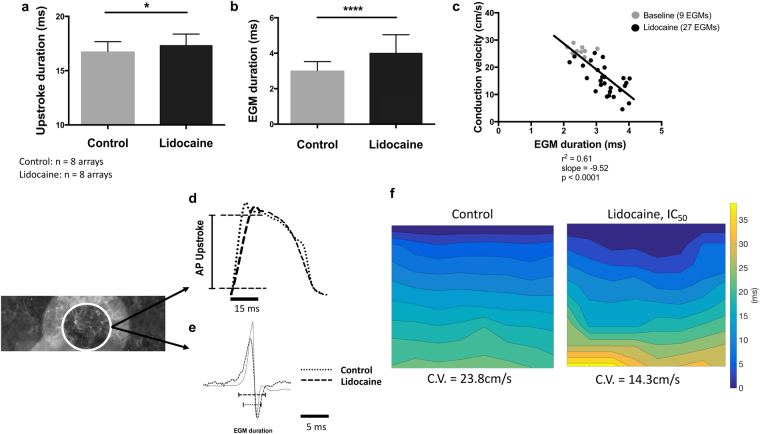
Figure 2.
Effects of lidocaine on action potential upstroke, electrogram duration and conduction velocity in NRVM cultures. Unpaired Student’s t-test (two-tailed) showing the effect of lidocaine (27 μmol/L) on upstroke duration (a) and EGM duration (b) measured before or after the addition of lidocaine (n = 8). (c) Correlation of upstroke duration with conduction velocity before or after sodium channel blockade (r2 = 0.6, p < 0.0001). (d) Superimposed optical action potentials showing increased upstroke duration after the addition of lidocaine, and (e) superimposed raw unipolar EGMs, which show decreased EGM amplitude and increased EGM duration due to the blockade of sodium channels, all derived from the same electrode as shown on the left. (f) Isochronal maps presenting the propagation of electrical activity before (23.8 cm/s) and after (14.3 cm/s) lidocaine administration in the same NRVM culture. All bar charts represent mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001.