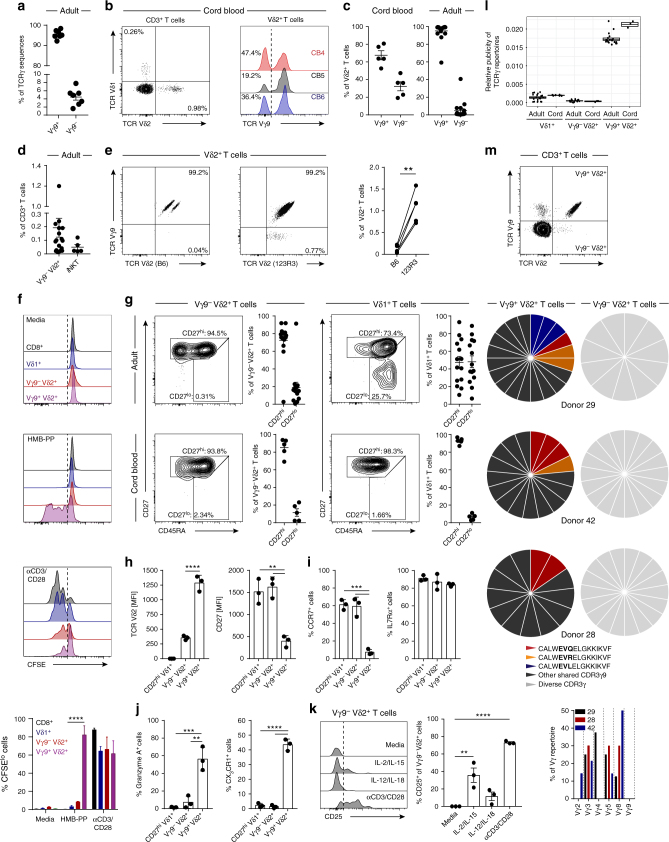
Fig. 3.
Vγ9− Vδ2+ T cells are clonally and phenotypically distinct from Vγ9+ Vδ2+ T cells. a Frequency of Vγ9 chain usage in Vδ2+ TCR repertoire sequencing data from adult peripheral blood (n = 7). b Identification of Vδ2+ T cells in CD3+ T cells (left) and Vγ9− cells within Vδ2+ T cells (right) from cord blood (n = 5). c Frequency of Vγ9− and Vγ9+ cells in Vδ2+ T cells from cord blood (left; n = 5) and adult peripheral blood (right; n = 18). d Frequency of Vγ9− Vδ2+ T cells (n = 18) and NKT cells (αGalcer/CD1d+; n = 5) in adult peripheral blood. e Vγ9− Vδ2+ T cells identified by TCR Vδ2 antibody clones (B6 and 123R3) in matched adult peripheral blood donors (n = 5). f Proliferation by CFSE dilution of CD8+ αβ and γδ T-cell populations from PBMC treated with medium alone, 10 nM HMB-PP or 5 μg/ml anti-CD3/CD28 (n = 5). g CD27 and CD45RA T-cell memory marker expression profiles on Vγ9− Vδ2+ and Vδ1+ T cells from adult peripheral blood (top row: Vδ2, n = 14; Vδ1, n = 14) and cord blood (bottom row: Vδ2 and Vδ1, n = 5). h Vδ2+ TCR and CD27 expression levels, i naive and j effector T-cell marker expression on donor matched γδ T-cell populations from adult peripheral blood (n = 3). k Sorted CD3+ T cells were incubated for 72 h with cytokines or anti-CD3/CD28 beads. Vγ9− Vδ2+ T cells were then assessed for the upregulation of CD25 (n = 3). l Comparison of CDR3γ sequence sharing in γδ T-cell repertoires from adult peripheral blood (Vδ1, n = 20; Vδ2, n = 7) and cord blood (Vδ1, n = 5; Vδ2, n = 3). m CDR3γ sequence analysis of single cell sorted Vγ9+ and Vγ9− Vδ2+ T cells, public sequences are coloured (black, shared sequences from deep sequencing); graph shows Vγ usage of Vγ9− Vδ2+ TCR sequences from each donor. Error bars indicate means ± SEM; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; p-values were determined by paired t-test (e), RM two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc testing (f); one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc testing (h, i) or Dunnett’s post hoc testing (j, k)