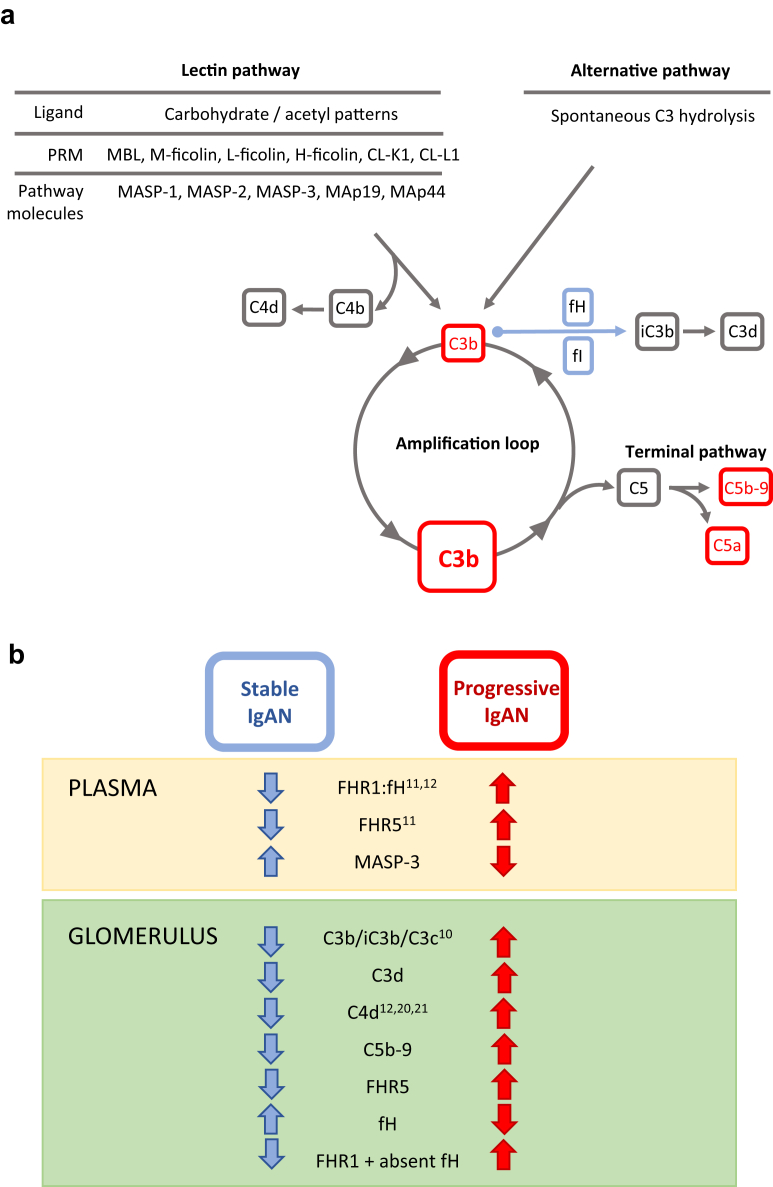
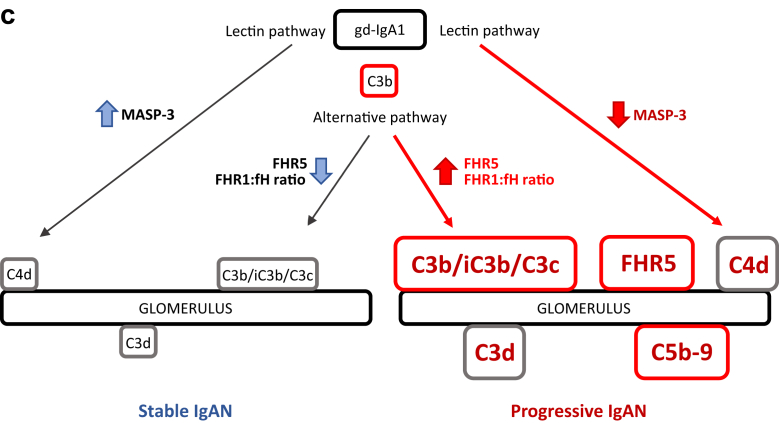
Figure 6.
Complement and IgA nephropathy. (a) Schematic diagram depicting lectin and alternative pathway complement activation. Lectin pathway activation is triggered by the binding of pattern-recognition molecules (PRMs) to carbohydrate or acetyl molecular patterns. Alternative pathway activation happens through the spontaneous, constant generation of reactive forms of C3. Both pathways result in the generation of C3b. C3b can be proteolytically cleaved to iC3b and C3d by complement factor I in the presence of cofactors, such as complement factor H. Similarly, C4b produced during lectin pathway activation can be cleaved to C4d. C3b generation can be rapidly amplified through an amplification loop. This results in the generation of large amounts of the opsonin C3b and can trigger complement C5 activation. This leads to the generation of the anaphylatoxin C5a, and the membrane attack complex (C5b-9) through the terminal pathway. fH, factor H; fI, factor I; MAp, MBL-associated protein; MASP, MBL-associated serine protease; MBL, mannose-binding lectin. (b) Complement proteins and severity of IgA nephropathy. Within plasma, increased levels of FHR1,11, 12 FHR5,11 and the FHR1:fH ratio11, 12 associate with progressive IgAN. Conversely, we found that reduced levels of MASP-3 associated with progressive disease. Within glomeruli, we replicated the association between increased C4d12, 20, 21 and C3b/iC3b/C3c10 with IgAN severity, and we showed that increased glomerular C3d, C5b-9, and FHR5 associated with progressive disease. The presence of FHR1 in the absence of fH was also more frequently seen in patients with progressive disease. FHR1, factor H–related protein 1; FHR5, factor H–related protein 5. (c) Hypothetical depiction of glomerular complement activation in IgA nephropathy. Galactose-deficient IgA1 (gd-IgA1) activates the lectin and alternative complement pathways in IgAN.8 Glomerular complement deposition is enhanced in progressive disease. Glomerular complement activation is influenced by FHR5 and the FHR1-fH ratio and associated with changes in circulating MASP-3 levels. Changes in FHR1, FHR5, and fH influence complement activation through the alternative pathway. fH negatively regulates activation, whereas FHR1 and FHR5 promote activation through antagonizing fH (“fH de-regulation”). The mechanism through which circulating MASP-3 levels fall in progressive disease are not understood but are presumed to be linked to lectin pathway activation. Red text highlights proteins demonstrated to associate with progressive IgAN and larger boxes indicate more deposition.