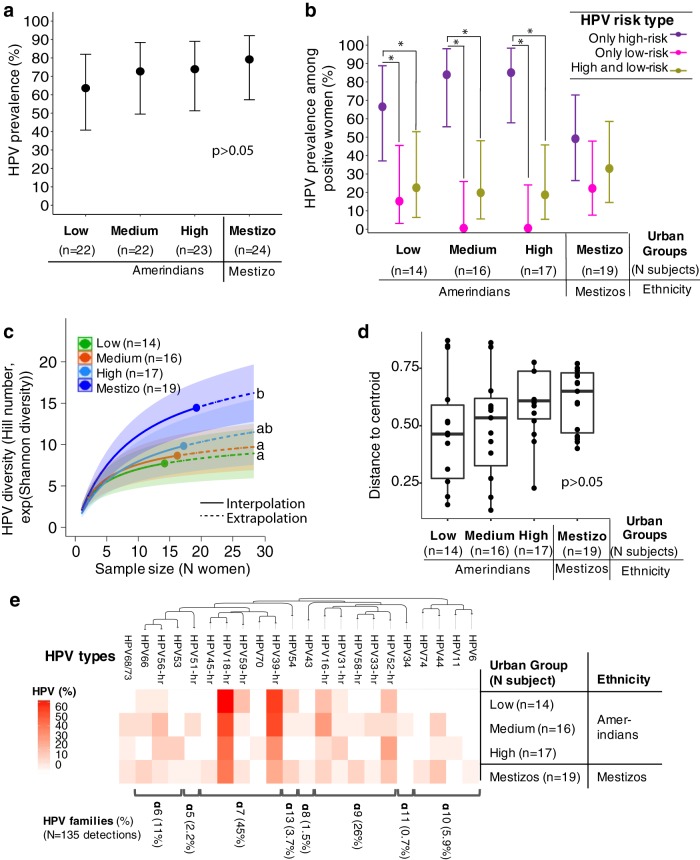
FIG 2 .
Prevalence and diversity of cervical HPV by subject-based urban groups. (a) HPV general prevalence. (b) HPV risk type prevalence. No prevalence differences were found among Amerindian groups (P = 0.540 by χ2 test) or between Amerindians from the high urban group and mestizos (P = 1.000 by χ2 test). Unlike mestizos, Amerindian women showed higher prevalence of only high-risk HPV types in relation to low-risk HPV or both types (P = 0.007 in the log linear model). The circles represent mean prevalence, and the bars show 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs). Prevalence that is statistically significantly (P < 0.050) different is indicated by a bar and asterisk. (c) Shannon diversity (Hill number q = 1) of cervical HPV by urban groups, based on a rarefied/extrapolated sample size of 28 women. Amerindians for low and medium urban groups were significantly less diverse than mestizos. There was a nonsignificant tendency to increasing HPV diversity with urbanization. The solid line curve fraction (interpolation) corresponds to the actual number of women sampled. The dashed line corresponds to the estimated diversity (extrapolation). Curved shaded areas represent the 95% CIs estimated from the bootstrap (50 replications). Significant differences are reached when 95% CIs do not overlap. Different letters indicate significant differences. (d) Beta diversity analysis by urban groups. Median distance to the centroid using Sorensen dissimilarity index. No difference among or within a group’s dispersion was observed (P > 0.05, PERMANOVA and permutation test for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions). (e) Heat map of prevalence of cervical HPV types. HPV18 and HPV39 of the α7 family showed the highest relative proportions. HPV L1 region sequences were used to generate a maximum likelihood tree rooted with theta HPV type (not shown). HPV families and their relative proportions (as a percentage; among only HPV-positive samples) are shown on the right. HPV68 and HPV73 were excluded from the tree, since the LiPA25 kit does not discriminate between these two types.