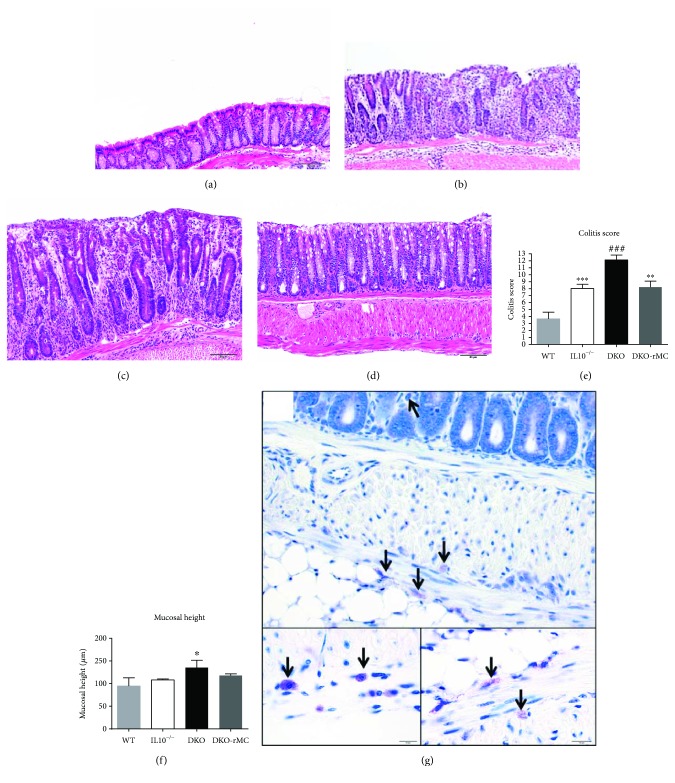
Figure 1.
Inflammation is exacerbated in the absence of mast cells and prevented by reconstitution with bone marrow-derived mast cells. Representative H&E-stained paraffin sections of the colon of 14-to-16-week-old wild-type C57Bl/6 (a), IL10−/− (b), mast cell-deficient colitis prone double knockout (DKO) (c), and DKO mice reconstituted with wild-type mast cells (DKO-rMC) (d). Colitis scores (e) and colonic mucosal height (f) are higher in DKO mice compared to IL10−/−, and mast cell reconstitution restores the colitis to the level of IL10−/− mice. Toluidine blue-stained sections confirming the reconstitution of tissue MCs (arrows) (g). WT: n = 5; IL10−/−: n = 25; DKO: n = 25; DKO-rMC: n = 13. ∗∗∗, ### p < 0.001; ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 versus DKO.