Figure 5. Cumulative incidence of suicide and nonfatal self-harm in the SOReg/Itrim study comparing gastric bypass with intensive lifestyle modification.
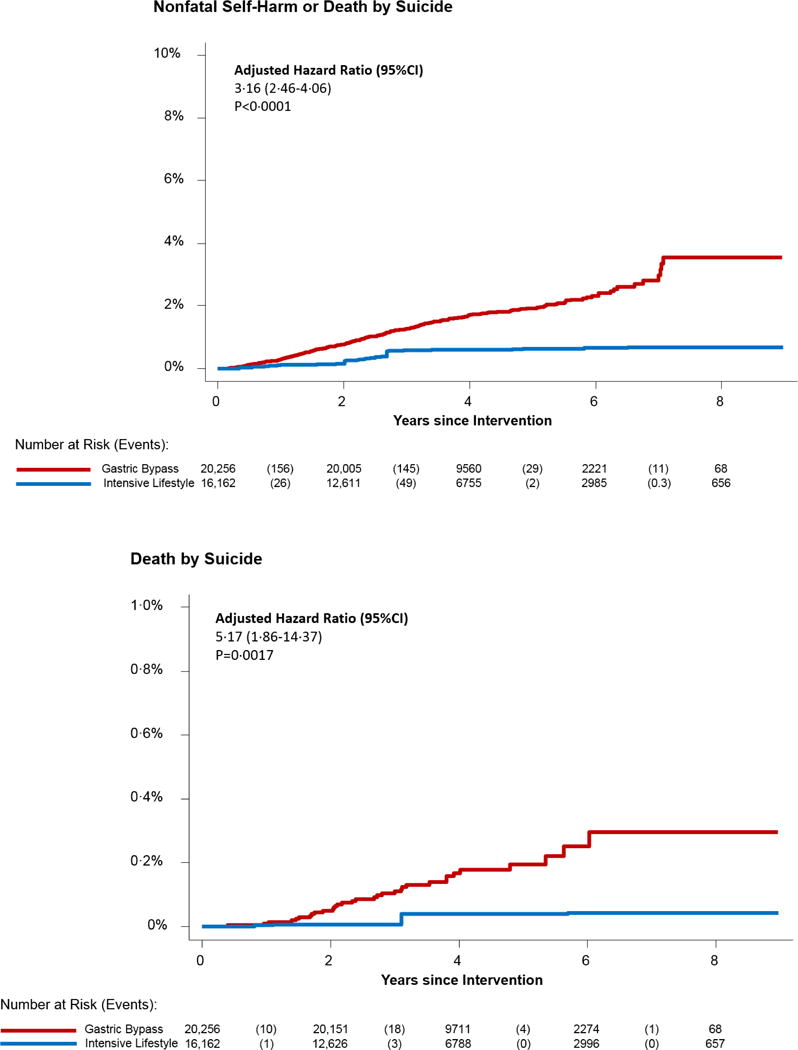
Matched on age, sex, BMI, education level, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, history of self-harm, substance abuse, visits in psychiatric care, use of antidepressants, and use of anxiolytics.
Hazard ratios adjusted for age, BMI, income, marital status, disability pension, and unemployment N for intensive lifestyle group are weighted by the strata size to account for the matching
