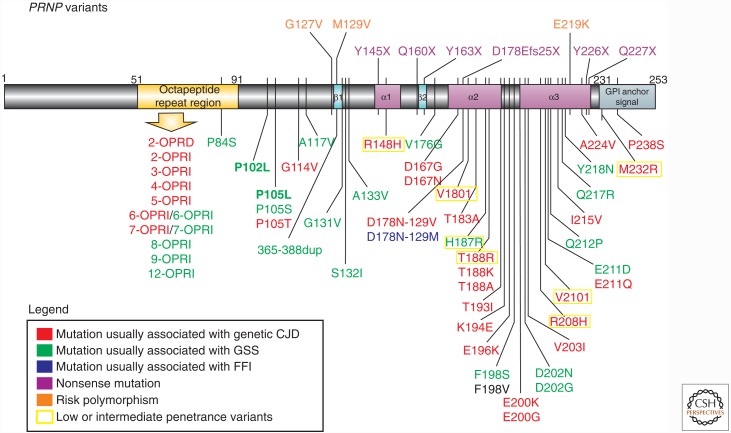
Figure 1.
Schematic of prion protein gene (PRNP) disease–associated variants. Mutations are color coded based on clinicopathological classification as genetic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (gCJD), Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker disease (GSS), familial fatal insomnia (FFI), or nonsense mutations. PRNP mutations present in the UCSF cohort are shown in bold. Most mutations are shown below the gene schematic; nonsense mutations and polymorphisms associated with prion disease risk are above the gene schematic. Low- or intermediate-penetrance variants are based on Minikel et al. (2016) (not all low/intermediate-penetrance variants are shown). For the F198V mutation, the clinical presentation was not classifiable as gCJD, GSS, or FFI (see Table 3), and neuropathology was not reported (Zheng et al. 2008). Variants that are most likely benign (largely based on Minikel et al. 2016) are not included (e.g., G54S, P39L, E196A, R208C) (Beck et al. 2010; Minikel et al. 2016). OPRI, Octapeptide repeat insertion; OPRD, octapeptide repeat deletion. (Reprinted from Takada et al. 2017.)