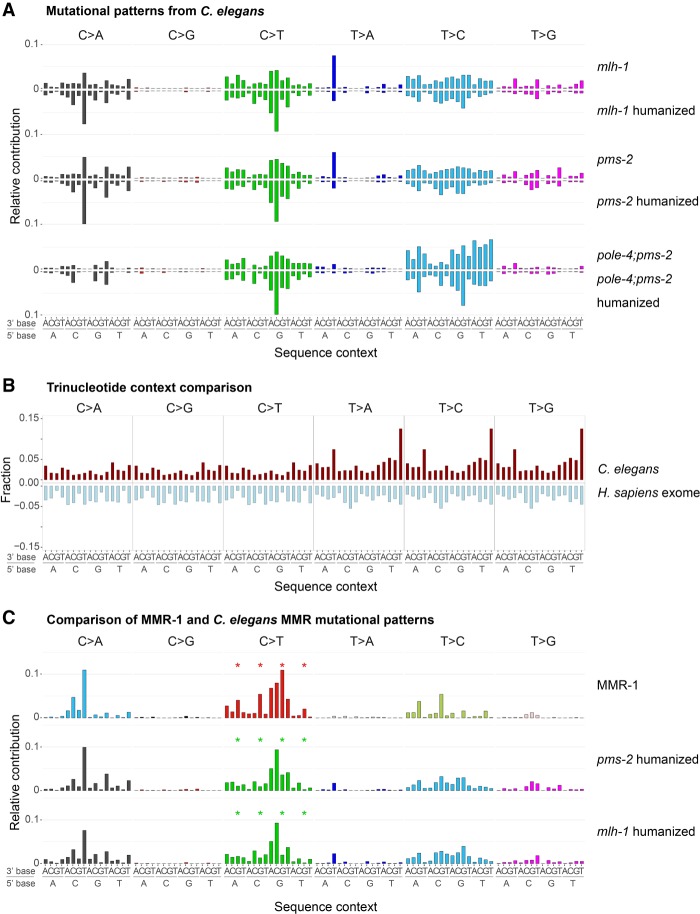
Figure 4.
Mutational patterns derived from C. elegans MMR mutants and their comparison to the de novo human signature MMR-1. (A) Base substitution patterns of C. elegans mlh-1, pms-2, and pole-4; pms-2 mutants and their corresponding humanized versions (mirrored). (B) Relative abundance of trinucleotides in the C. elegans genome (red) and the human exome (light blue). (C) MMR-1 base substitution signature compared to pms-2 and mlh-1 mutational patterns adjusted to human whole-exome trinucleotide frequency. Stars indicate the difference in C > T transitions at CpG sites, which occur at lower frequency in C. elegans.