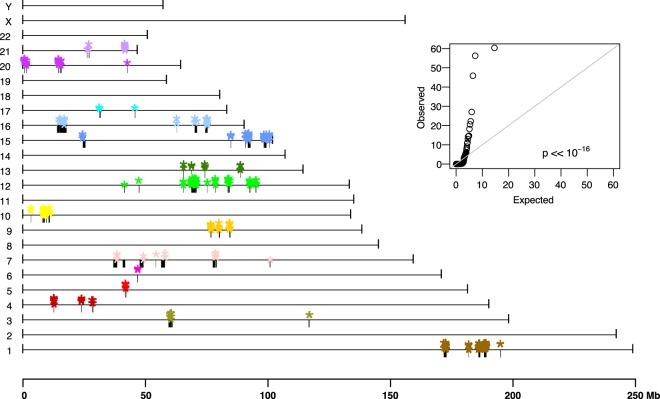
Figure 9.
Fusion clusters. Donor fragments (black bars) and complex genomic rearrangement breakpoints (colored stars) found in the 72 fusion maps are highly localized on the reference genome map, GRCh38. Fusion breakpoints on some chromosomes are notably at the boundaries of reference donor fragments (e.g., Chromosomes 15 and 20), suggesting that acquisitions of these fragments in the rearranged genomes were late events. This is in contrast to donor fragments with “internal” CGRs (e.g., Chromosome 12), suggesting their acquisitions were early events. The inset is a quantile–quantile plot of the observed adjacent fusion breakpoint distances relative to the null expectation of random distribution, indicating the distribution of fusion breakpoints is statistically significantly nonrandom. Colors of plotting symbol correspond to the default UCSC chromosome color scheme.