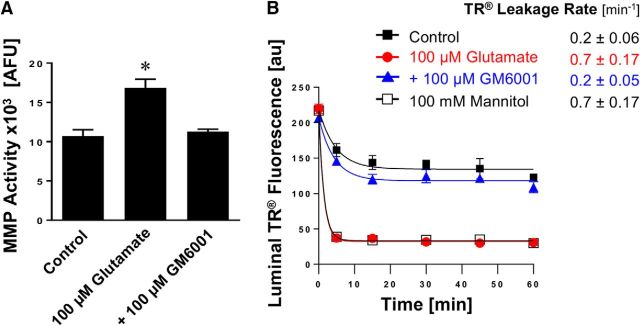
Figure 5.
Effect of inhibiting MMPs on glutamate-mediated barrier leakage. A, Total MMP enzyme activity in brain capillaries was assessed by using the fluorogenic substrate Mca-PLGL-Dpa-AR-NH2. MMP activity was measured in lysate from isolated brain capillaries exposed to 100 μm glutamate with or without the MMP inhibitor GM6001. MMP activity is given as AFU; data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments; pooled tissue of 10 rats per experiment). Statistical comparison: *control: 10.7 ± 0.6 AFU; glutamate: 16.8 ± 0.8 AFU; glutamate + GM6001: 11.3 ± 0.2 AFU; glutamate + GM6001 versus control: t(2) = 0.69, p = 0.56; glutamate + GM6001 versus glutamate: t(2) = 4.83, p = 0.04 (ANOVA post hoc tests). B, Texas Red leakage was measured in capillaries exposed to 100 μm glutamate with or without the MMP inhibitor GM6001.