Figure 6.
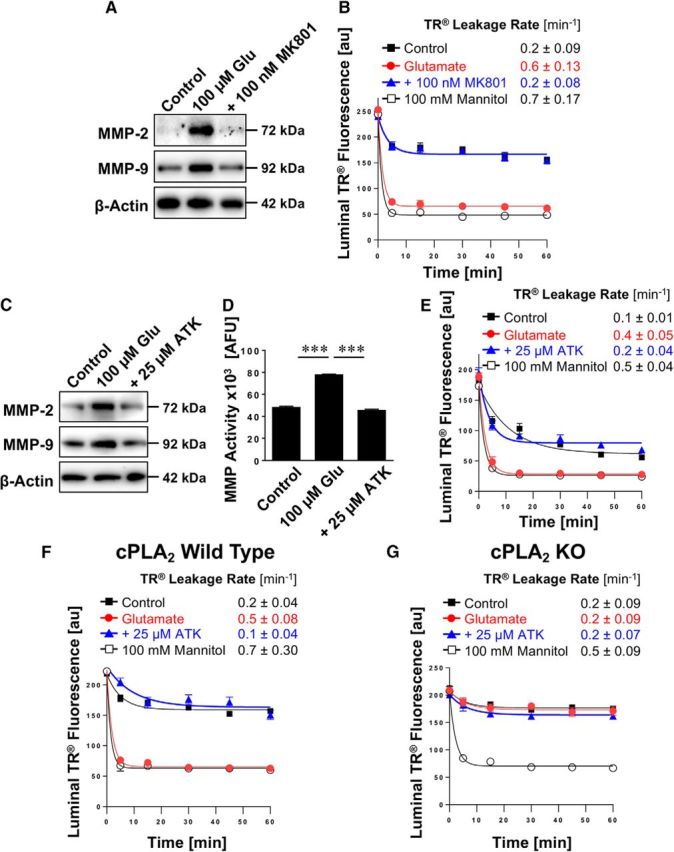
Effect of inhibiting cPLA2 on glutamate-mediated MMP-2 and MMP-9 induction and barrier leakage. A, Western blots showing MMP-2 and MMP-9 protein expression in isolated rat brain capillaries exposed to 100 μm glutamate with or without the NMDAR antagonist MK801. β-Actin was used as protein loading control. B, Texas Red leakage assay showing glutamate-mediated barrier leakage with or without the NMDAR antagonist MK801. C, Western blots showing MMP-2 and MMP-9 protein expression levels in isolated rat brain capillaries exposed to 100 μm glutamate with or without the cPLA2 inhibitor ATK. β-Actin was used as protein loading control. D, MMP activity assessed in isolated capillaries exposed to 100 μm glutamate with or without ATK (ATK vs control: t(2) = 3.08, p = 0.091; ANOVA post hoc test). E, Texas Red leakage assay showing glutamate-mediated barrier leakage with or without ATK (cPLA2 inhibitor). Texas Red leakage assay in capillaries from (F) wild-type and (G) cPLA2 KO mice that were exposed to 100 μm glutamate with or without the cPLA2 inhibitor ATK. Data are 0–255 AFU and presented as mean ± SEM for n = 7 brain capillaries per time point from one capillary isolation with n = 10 rats or n = 30 mice, respectively. ***Significantly higher than control, p < 0.001.
