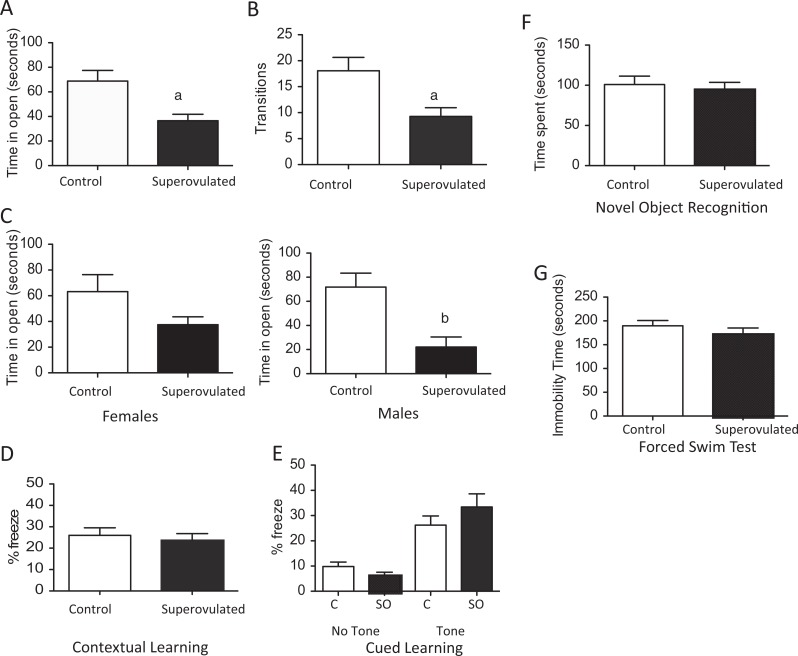
Figure 5.
Behavioral testing of adult offspring resulting from control recipient (white bar) or superouvlated recipient (black bar). Elevated zero maze testing showed offspring of superovulated recipients had significantly less time in open areas (A) and fewer transitions into the open area than offspring from control mice (B). This was true for both male and female mice (C). There was no difference in learning or memory between the groups by contextual or cued learning (D and E) or by novel object recognition (F). There was also no change in depressive behaviors by forced swim test (G). (Control: n = 25, 9 females and 16 males; Superovulated: n = 23, 16 females and 7 males) a P < .01 versus offspring of control recipients. b P < .05 versus offspring of control recipients. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).