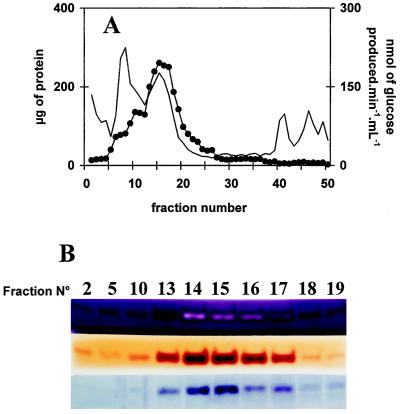
Figure 3.
Co-purification of starch structure modification, Glc production from maltotriose, and incorporation of maltoheptaose into the external chains of glycogen. A, Elution profile of FPLC chromatography. In this experiment, 60 mg of crude extract protein (after a protamine sulfate precipitation step) was loaded on an anion-exchange column linked directly to a cation-exchange column, which was only eluted with 5% (w/v) NaCl. Two-milliliter fractions were collected at a 1 mL min−1 flow rate. Proteins (thin line) were measured in each fraction according to the Bio-Rad assay. D-enzyme activity (•) was monitored through production of Glc from maltotriose (see Methods). B, Fractions from all cation exchanges were assayed through three distinct zymogram procedures involving denaturation of proteins and renaturation after migration (see Methods). Only the active fractions are shown in B. Three distinct zymogram procedures are displayed. These include modification of starch structure (top), incorporation of maltoheptaose in the outer chains of glycogen (middle), and Glc production from maltotriose (bottom). All active bands were shown to migrate as 62-kD proteins. Note that the dark-red band that characterizes D-enzyme in starch-containing zymograms turns to a white stain upon incubation with a vast excess of enzyme in the concentrated peak fractions.