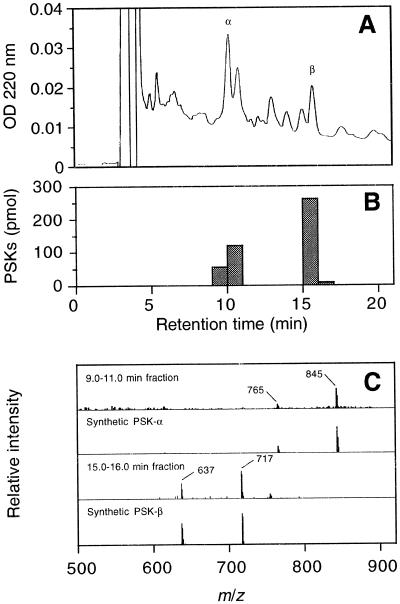
Figure 5.
Identification of PSKs in conditioned medium derived from zinnia mesophyll cell culture. A, HPLC profile of purified conditioned medium. Conditioned medium derived from TE-inductive culture was separated by two steps of open-column chromatography and reverse-phase HPLC. Fractions were collected every minute. B, Results of competitive ELISA. The amount of PSKs contained in each fraction was determined by competitive ELISA based on anti-PSK-α antibodies. Peaks eluting at 10.2 and 15.7 min were estimated to be PSK-α and PSK-β, respectively. C, Comparison of mass spectrum of natural sample and synthetic PSK-α. A combined fraction (9.0–11.0 min) was concentrated and analyzed by MS (1st row). A pseudomolecular ion of m/z 845 corresponds to [M-H]− and a fragment ion of m/z 765 corresponds to [M-H-80]− of PSK-α, coinciding well with the spectrum of synthetic PSK-α (2nd row). A fraction (15.0–16.0 min) was concentrated and analyzed by MS (3rd row). A pseudomolecular ion of m/z 717 corresponds to [M-H]−, and a fragment ion of m/z 637 corresponds to [M-H-80]− of PSK-β, coinciding well with the spectrum of synthetic PSK-β (4th row).