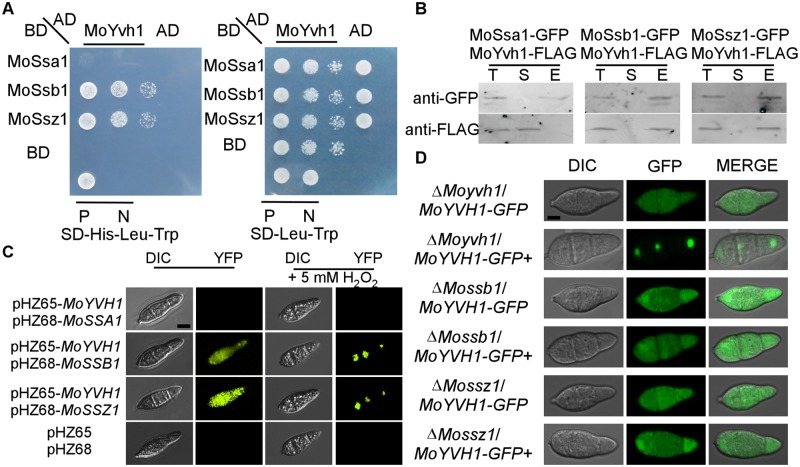
Fig 2. MoSsb1 and MoSsz1 are required for the translocation of MoYvh1 to the nucleus under oxidative stress.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of interactions between MoYvh1 and MoSsa1, MoSsb1, and MoSsz1. MoYvh1 cDNA was inserted into the vector pGADT7, whilst MoSsa1, MoSsb1, and MoSsz1 cDNA was inserted into pGBKT7. “P” represents positive controls and “N” represents negative controls. Yeast cells grown on synthetic dextrose (SD) medium lacking leucine (Leu), tryptophan (Trp) and Histidine (His) were investigated against positive and negative controls as indicated. Plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 days before being photographed. (B) Co-IP assay. Western blot analysis of total proteins (T) extracted from conidia of various transformants, suspension proteins (S) and elution proteins (E) eluted from anti-GFP beads. The presence of MoYvh1, MoSsa1, MoSsb1 and MoSsz1 was detected with the anti-GFP and anti-FLAG antibodies, respectively. (C) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for interactions between MoYvh1 and Hsp70 homologs. Conidia of transformants expressing MoYvh1-NYFP and Hsp70s-CYFP constructs (left panels) were treated (right panels) with 5 mM H2O2 for 2 h before interference contrast (DIC) and epifluorescence microscopy. YFP, yellow fluorescent protein. Bar = 5 μm. (D) Localization of MoYvh1-GFP was visualized in conidia of the ΔMossb1, ΔMossz1 and ΔMoyvh1 mutants. “+” represents the samples treated with 5 mM H2O2 for 2 h. Bar = 5 μm.