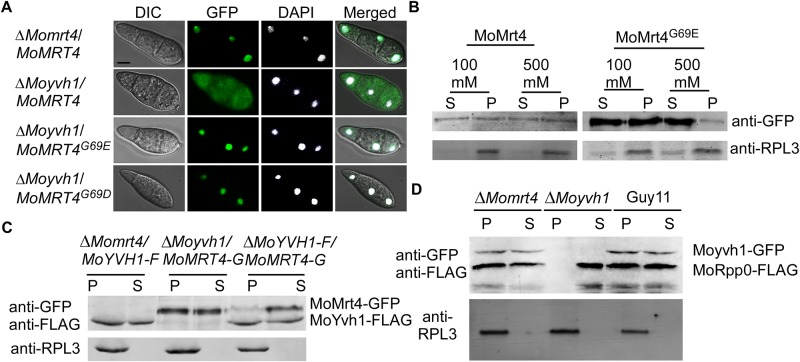
Fig 4. Dissociation of MoMrt4 from the pre-ribosome in the nucleolus facilitated by MoYvh1 is required for the ribosome maturity.
(A) The localization of Mrt4-GFP, MoMrt4G69D-GFP and MoMrt4G69E-GFP was observed in conidia of the ΔMomrt4 and ΔMoyvh1 mutants. DAPI was used to stain nuclei. The merged image of GFP and DAPI staining showed that ΔMoyvh1/MoMRT4–GFP, ΔMoyvh1/MoMRT4G69D-GFP and ΔMoyvh1/MoMRT4G69E-GFP strains were localized in the nucleus. Bar = 5 μm. (B) Ribosomal proteins were prepared from ΔMoyvh1/MoMRT4–GFP and ΔMoyvh1/MoMRT4G69E-GFP strains grown at as indicated salt concentrations. Free and ribosome-bound proteins were separated by sedimentation through sucrose cushions. Equal amounts of supernatant (S) and pellet (P) were separated by SDS-PAGE, and the presence of MoMrt4 and Rpl3 (a ribosome marker) was detected by Western blotting analysis using anti-GFP or anti-RPL3 antibodies. (C) Ribosome proteins were extracted from the strains as indicated. Free and ribosome-bound proteins were separated by sedimentation through sucrose cushions. Both the anti-GFP and anti-FLAG antibodies were added to detect the presence of MoMrt4 and MoYvh1 in supernatants (S) and pellets (P) following SDS-PAGE. RPL3 was used as a marker for ribosome. (D) Ribosome proteins of the indicated strains were extracted. Equal amounts of supernatant (S) and pellet (P) were separated by SDS-PAGE, and MoRpp0 and MoYvh1 were detected by Western blotting using anti-GFP and anti-FLAG antibodies.