Extended data Figure 7. Analysis of Gypsy splicing in OSC cells.
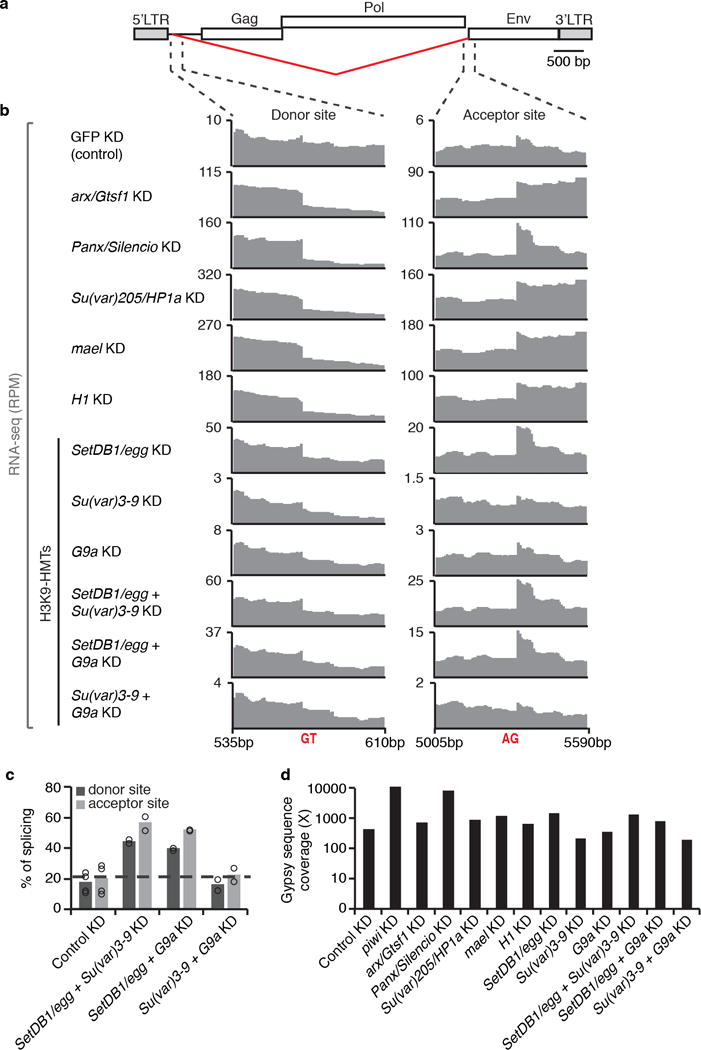
a, Diagram of Gypsy retrotransposon, as in Figure 4a. b, RNA-seq signal (RPM) at the Gypsy splicing donor and acceptor sites in representative control (GFP KD) and KDs of arx/Gst1, Panx/Silencio, Su(var)205/HP1a, mael, histone H1, SetDB1/egg, Su(var)3-9, G9a. Data for double KDs of SetDB1/egg + Su(var)3-9, SetDB1/egg + G9a, and Su(var)3-9 + G9a are also shown. With the exception arx/Gst1, Su(var)205/HP1a, mael, and H17,25, experiments were repeated two times with similar results. c, Percentage of splicing for Gypsy donor and acceptor splicing sites as determined by RNA-seq analysis performed in OSC cells double KDs of H3K9 methyltransferases. Bars represent the number of split-reads for the env donor and acceptor splicing junctions normalized to the total number of sense Gypsy reads mapping to the same junction. Results are represented as means. Experiments were repeated two times with similar results. d, Coverage of Gypsy consensus sequence by RNA-seq data. Coverage was calculated as: [number of reads matching Gypsy consensus sequence × read length in nucleotides]/Length of consensus Gypsy sequence in nucleotides (7469nt). Raw data sets from Ohtani et al, 20137; Sienski et al, 20159; Iwasaki et al, 201625.
