Figure. Associations of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia with elevated liver enzymes and PNFI.
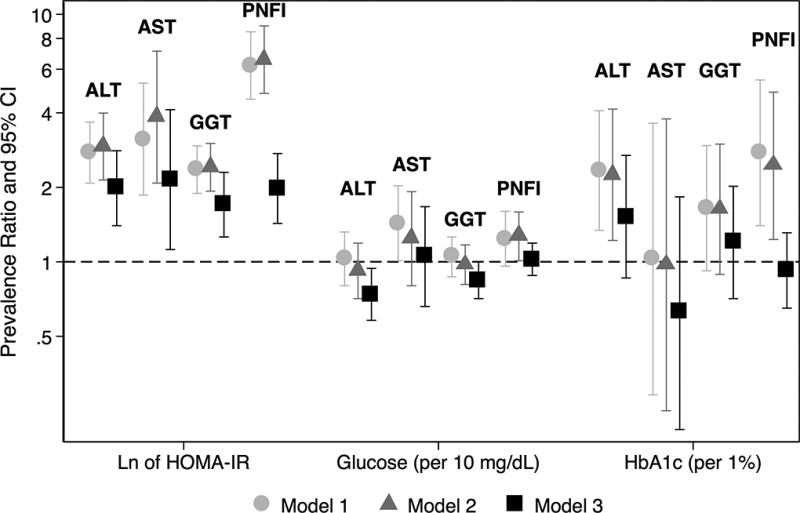
Elevated liver enzymes were defined as ALT >25 U/L for boys and >22 U/L for girls, AST ≥37 U/L, GGT ≥17 U/L. Elevated PNFI was defined as ≥9. Prevalence ratios were obtained using Poisson regression models with robust variance. We specified the models as follows: Model 1: Unadjusted; Model 2 (Sociodemographics): Model 1 + age, sex, Mexican background, field center, household income, and parental education; Model 3 (traditional risk factors): Model 2 + moderate/vigorous activity, elevated waist circumference, BMI percentile, systolic blood pressure percentile, LDL-c, HDL-c, ln of triglycerides, and pubertal status. Models for PNFI were not adjusted for age, waist circumference, or triglycerides, since PNFI is calculated using these variables.
