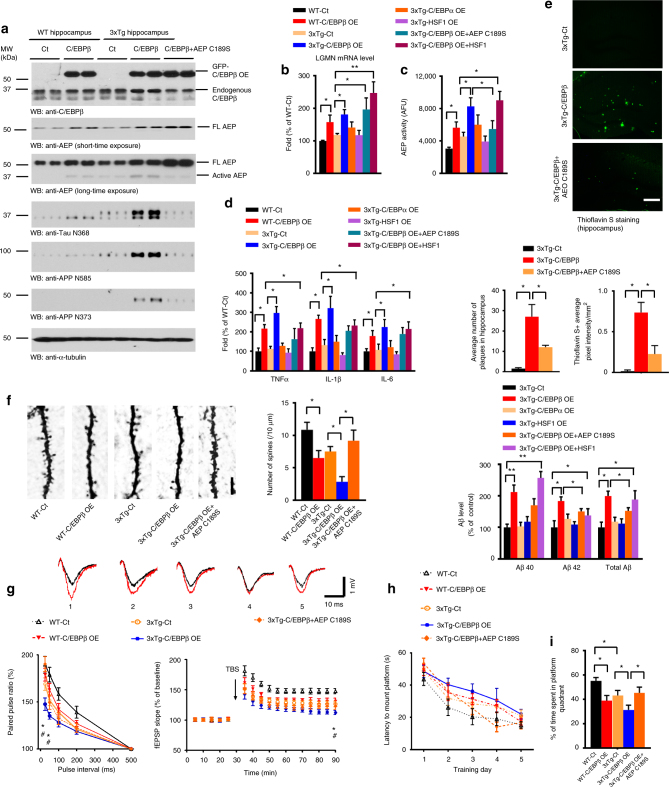
Fig. 5.
Overexpression of C/EBPβ in young 3xTg mice accelerates the onset of AD-like pathogenesis and worsens cognitive dysfunctions. a Overexpression of C/EBPβ escalates delta-secretase and APP and Tau cleavage. Hippocampal tissues were analyzed by immunoblotting. C/EBPβ-induced active delta-secretase was antagonized by the co-expression of C189S mutant (n = 3 mice per group). b, c Overexpression of C/EBPβ but not C/EBPα increases delta-secretase mRNA and enzymatic activities. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. of three mice per group (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA). d Overexpression of C/EBPβ but not C/EBPα increases the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. of three mice per group (*P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). e C/EBPβ overexpression enhances the early formation of amyloid plaques in 3xTg mice. Thioflavin S staining for the senile plaques (top, scale bar, 50 μm). Analysis data (middle) represent mean ± s.e.m. of 12–18 sections from three mice per group and Aβ ELISA (lower) represent mean ± s.e.m. of three mice per group (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA). f Overexpression of C/EBPβ decreases dendritic spine density. Golgi staining was conducted on brain sections from apical dendritic layer of the CA1 region. Scale bar, 5 μm. Data (right) represent mean ± s.e.m. of 9–12 sections from three mice in each group. (*P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). g Electrophysiology analysis. C/EBPβ overexpression worsened the LTP defects in 3xTg mice. The ratio of paired pulses (mean ± s.e.m.; n = 6 in each group; *P < 0.05 compared with 3xTg-Ct, #P < 0.05 compared with 3xTg-C/EBPβ+AEP C189S, one-way ANOVA) (left). LTP of fEPSPs (mean ± s.e.m.; n = 6 in each group; *P < 0.05 compared with 3xTg-Ct, #P < 0.05 compared with 3xTg-C/EBPβ+AEP C189S, one-way ANOVA) (right). Shown traces are representative fEPSPs of 10 samples recorded before (black) and after (red) TBS (theta-burst stimulation). 1, WT-Ct; 2, WT-C/EBPβ OE; 3, 3xTg-Ct; 4, 3xTg-C/EBPβ OE; 5, 3xTg-C/EBPβ+C189S AEP. h, i Morris water maze analysis. C/EBPβ overexpression exacerbated the learning and memory dysfunctions (mean ± s.e.m.; n = 7–8 mice per group; *P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA)