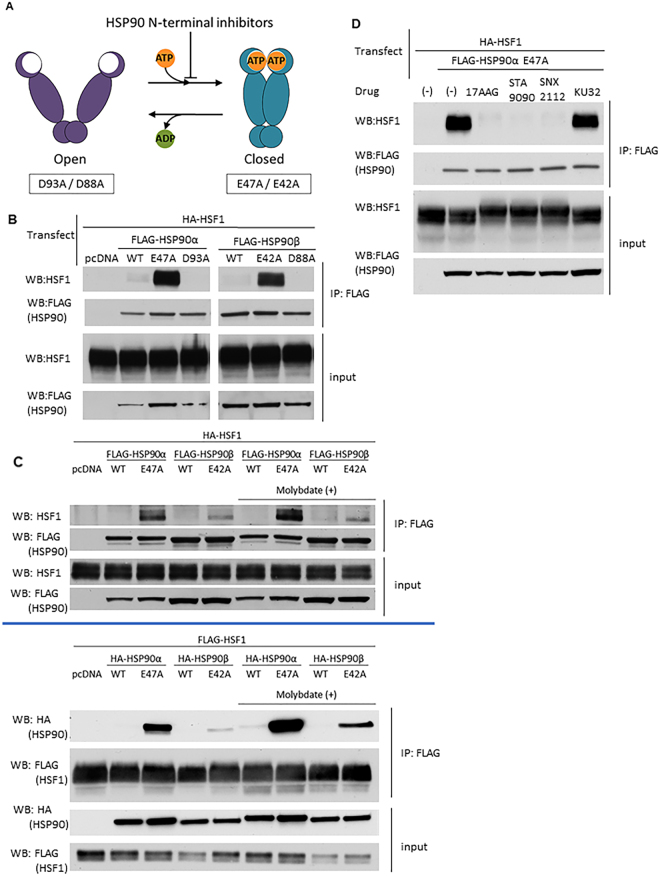
Figure 1.
HSF1 is bound by HSP90 in the “closed” conformation. (A) HSP90 ATP-driven conformational cycle. HSP90α E47A/HSP90β E42A mutants bind ATP but cannot hydrolyze it and remain trapped in the “closed” N-domain dimerized conformation. Conversely, HSP90α D93A/HSP90β D88A mutants do not bind ATP and remain trapped in an “open” N-domain undimerized conformation. (B) HSF1 interaction with HSP90 “closed” and “open” mutants. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with HA-HSF1 and with each FLAG-HSP90 construct, harvested and analyzed for HSF1/HSP90 association by anti-FLAG IP - HSF1 WB. Pull-down experiments were repeated at least twice. (C) Reproducible and reciprocal HSF1 interaction with “closed” HSP90α E47A and HSP90β E42A mutants in the presence and absence of MoO4. Interactions were assessed by anti-FLAG (HSP90) IP - HSF1 WB (top panel) or anti-FLAG (HSF1) IP–HA (HSP90) WB (bottom panel). Pull-down experiments were repeated at least twice. (D) Effect of HSP90 inhibitors on HSF1-HSP90α E47A interaction. HEK293 cells were transfected with HA-HSF1 along with FLAG-HSP90α E47A, treated with N-terminal or C-terminal HSP90 inhibitors for 4 hours and analyzed by anti-FLAG (HSP90) IP- HSF1 WB. Pull down experiments were repeated at least twice. Full blots used to create cropped figure panels are shown in Supplementary Figure 6.