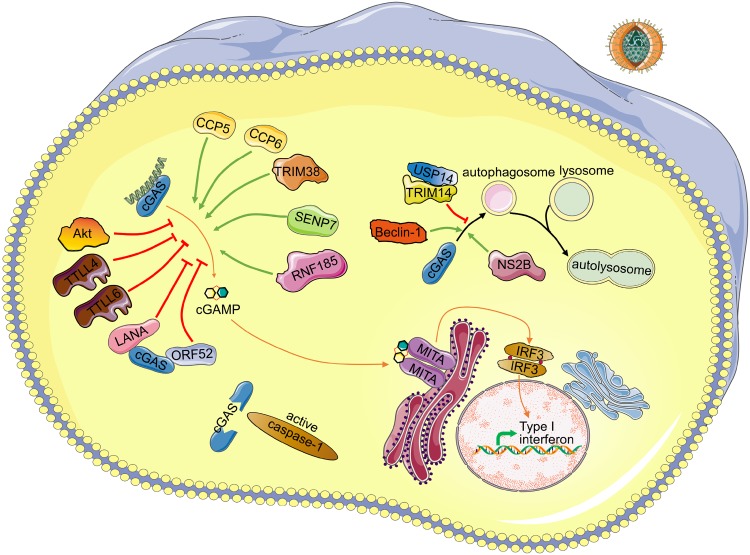
Fig. 1.
Schematic regulating network of cGAS. Detailed regulating proteins and virus antagonist of cGAS are depicted. Upon DNA binding to cGAS, cGAMP is synthesized by cGAS from ATP and GTP. Then binding of cGAMP to the adapter MITA induces conformational changes of MITA homodimer, leading to production of cytokines including type I interferons. Green arrows indicate positive regulators of the corresponding process. Red arrows indicate negative regulators of the corresponding process. Upon inflammasome activation, caspase-1 inhibits the cGAS-MITA pathway by cleavage of cGAS. DENV NS2B protein promotes the autophagy–lysosome-dependent degradation of cGAS. TRIM14 and USP14 inhibit the degradation of cGAS by cleaving K48-linked ubiquitin chains of cGAS. Beclin-1 promotes the autophagic degradation of cGAS. CCP5/6, TRIM38, SENP7 and RNF185 promote the activity of cGAS by deglutamylation, SUMOylation, deSUMOylation, ubiquitination of cGAS, respectively. TTLL4, TTLL6 and Akt inhibit the activation of cGAS by monoglutamylation, polyglutamylation, phosphorylation of cGAS, respectively. LANA of KSHV interacts and antagonizes cGAS. ORF52 of KSHV interacts with cGAS and inhibits the enzymatic activity of cGAS.