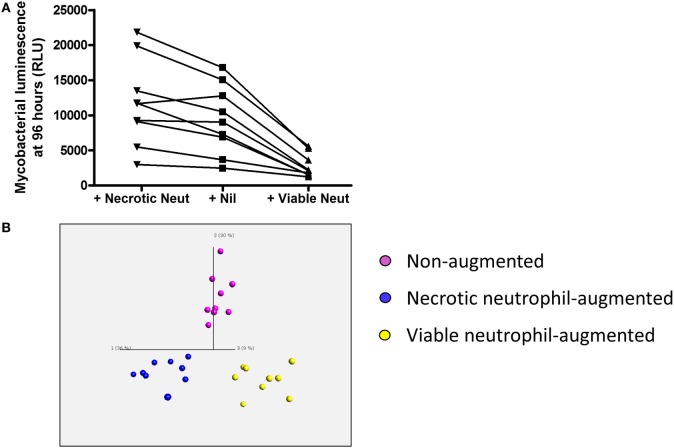
Figure 3.
Impact of viable and necrotic neutrophil augmentation on control of mycobacterial luminescence by whole blood and on supernatant cytokines and chemokines from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected blood. (A) 100,000 RLU of M. tuberculosis-lux in 100 mcl PBS was inoculated into samples of 450 mcl whole blood plus either 450 mcl Percoll-isolated autologous neutrophils in RPMI-1640 heat-shocked at 60°C for 20 min and allowed to cool (“+Necrotic Neut”), 450 mcl RPMI-1640 only (“+Nil”), or 450 mcl room temperature Percoll-isolated autologous neutrophils in RPMI-1640 (“+Viable Neut”). After 96-h incubation, red blood cells were lysed and luminescence was measured on at least two aliquots of 100 mcl. Results are shown from nine independent donors. (B) Three-dimensional principal component analysis (PCA) plot generated using cytokine/chemokines that significantly contribute to differentiation between supernatants of augmentation conditions (calculated using multi-group comparison; purple = non-augmented, blue = necrotic neutrophil-augmented, yellow = viable neutrophil-augmented). PCA is a technique to reduce the dimensionality of complex datasets by transforming the data to a coordinate system. The first three coordinates (principal components) are represented as a 3D plot. The first principal component accounts for as much variability as possible within the data, and each succeeding component accounts for the next highest proportion of the variability possible, but under the constraint that it is not correlated with preceding components. This allows visualization of the differences between patient samples and analytes within complex datasets. Individual points represent one donor in one augmentation condition and their position in the plot is determined by the combined effects of all parameters measured for the sample that significantly contribute to the overall between-group difference. Component vectors for the three main components are displayed, along with a percentage figure signifying the proportion of the variability in the data that each component accounts for. Analysis is presented using raw values from infected supernatants.