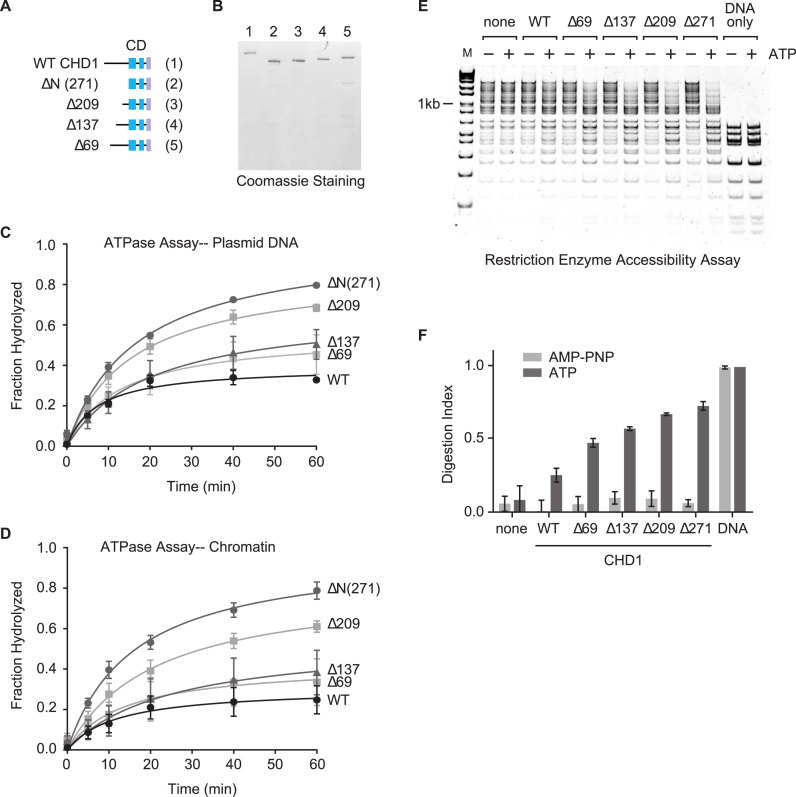
Figure 5.
A step-wise loss of the N terminus of CHD1 leads to a length-dependent increase in enzymatic activity. (A and B) A series of deletions from the N terminus was expressed and purified, similar to the WT CHD1 protein. The schematic only highlights the N terminus although the full-length proteins minus the deletion were expressed. Time-course ATPase assays using either plasmid DNA (C) or a chromatin substrate (D) as a cofactor were performed using the N terminal deletion proteins. (E) Successive deletions from the N terminus of CHD1 lead to a step-wise increase in the remodeling activity of CHD1 as measured by REA. (F) Quantification of the REA assays shown in (E). Mean and SD of the digestion index (DI) from three experiments are shown.