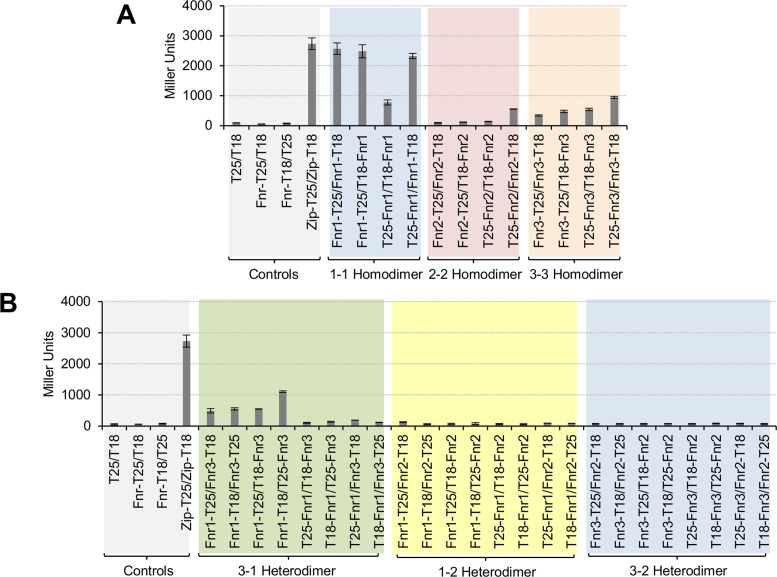
Figure 3.
Heterodimers between Fnr1 and Fnr3 proteins are formed in vivo. (A) β-Galactosidase activity from the BACTH assay to test the homodimerization of Fnr1, Fnr2 and Fnr3. The interaction between Fnr proteins was tested using all possible combinations of fusion proteins. Negative controls: empty two-hybrid vectors (T25/T18); Fnr-T25 fusion protein combined with the empty vector carrying the T18 subunit (Fnr-T25/T18) and the Fnr-T18 fusion protein combined with the empty vector carrying the T25 subunit (Fnr-T18/T25). Fnr-T25/T18 and Fnr-T18/T25 denote that all three Fnr fusion proteins were tested for the unspecific interaction with either T18 or T25 fragments. The data shown is the average activity for all possible combinations. Positive control: we used the leucine zipper domain fusion proteins from the BACTH system (Zip-T25/Zip-T18). (B) β-galactosidase activity from the BACTH assay to test heterodimerization between different heterologous pairs of Fnr proteins (Fnr3–Fnr1, Fnr1–Fnr2 and Fnr3–Fnr2). For each Fnr pair, all eight possible pairwise combinations of fusion proteins were tested. The graph is shaded in different colours to facilitate identification of the different sets of interactions tested. β-galactosidase assays were performed using cultures grown under oxygen-limiting conditions. Error bars show standard deviation of three independent biological replicates carried out for each pairwise combination.