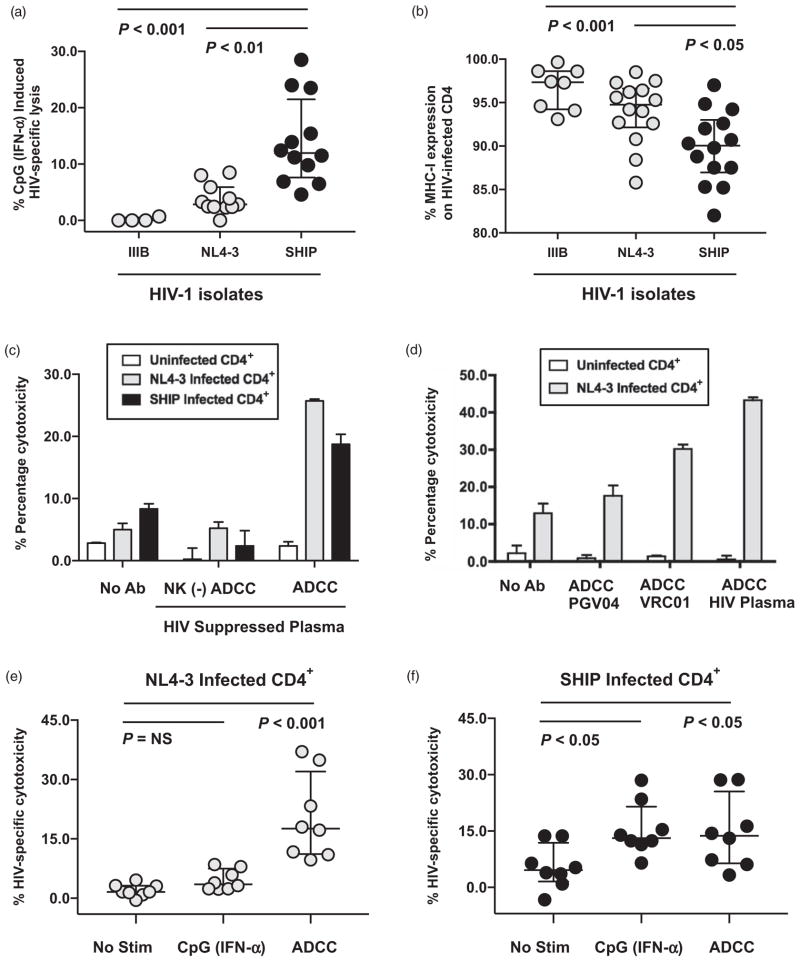
Fig. 1. Antibodies against HIV gp120 can trigger natural killer-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity lysis of HIV-1-infected autologous CD4+ T cells independently of MHC-I downregulation.
(a) Composite data from multiple donors measuring HIV-specific lysis of IIIB, NL4-3, or 96USHIPS9 (SHIP) infected autologous CD4+ primary T cells by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) following CpG-ODN 2216 stimulation at a 100 : 1 effector-to-target cell ratio in a standard 4-h chromium lysis assay. A total 10 μg/ml CpG-2216 was added to PBMCs 18 h prior to chromium lysis assay to stimulate plasmacytoid dendrtitic cells to secrete endogenous IFN-α that activates natural killer cells and triggers cytotoxicity [21]. CpG (IFN-α) induced lysis was calculated after subtracting lysis by unstimulated PBMCs from the same donor tested in parallel. HIV-specific cytotoxicity was calculated as lysis of HIV-1-infected CD4+ primary T cells minus background lysis of uninfected CD4+ primary T cells. Statistical analysis of three groups was carried out with a Kruskal–Wallis unpaired, nonparametric analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Dunn posttest and a two-tailed P value. (b) Composite analysis of HIV-specific MHC-I downregulation as determined by measuring the percentage of HLA-A, B, and C expression on HIV-1 infected (p24 positive cells) in each experiment relative to mock uninfected cells (set at 100%). PHA/IL-2 stimulated CD4+ primary T cells were infected with either laboratory adapted (IIIB or NL4-3) or primary (SHIP) HIV-1 isolates for 4 days, stained with antibodies to MHC class I (pan W6/32), and permeabilized for intracellular p24 expression by flow cytometry. Statistical analysis of three groups was carried out with a Kruskal–Wallis unpaired, nonparametric ANOVA with a Dunn posttest and a two-tailed P value. (c) 4-h standard chromium release assay measuring the ability of total or natural killer–depleted (−) PBMCs to mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) lysis against uninfected (white), HIV-1 NL4-3 (light gray), or HIV-1 SHIP infected (black) autologous CD4+ primary T cells at a 100 : 1 effector-to-target cell ratio in the presence or absence of a 1/1000 dilution of plasma from a representative HIV-1-infected ART-suppressed patient. (d) ADCC chromium release assay measuring the percentage cytotoxicity of uninfected or NL4-3-infected autologous CD4+ primary T cells by PBMCs at a 100 : 1 effector/target ratio in the presence or absence of 10 μg/ml PGV04 or 10 μg/ml VRC01 monoclonal antibodies to gp120 or a 1/1000 dilution of plasma from a representative HIV-1-infected ART suppressed patient (HIV plasma) to trigger ADCC. (e and f) Composite data from multiple donors measuring HIV-specific natural killer lysis of NL4-3 (e) or SHIP (f) infected autologous CD4+ primary T cells in the presence of different stimuli. Direct lysis in the absence of stimulation (no stim) was compared with 10 μg/ml CpG-2216 (IFN-α) induced direct lysis and to ADCC lysis (triggered with a 1/1000 dilution of plasma from a representative HIV-1-infected ART suppressed patient). HIV-specific cytotoxicity was calculated as lysis of HIV-1 infected CD4+ primary T cells minus background lysis of uninfected CD4+ primary T cells. Statistical analysis of three groups was carried out with a Friedman paired, nonparametric ANOVA with a Dunn posttest and a two-tailed P value.