Figure EV4. Allosteric activation of SERCA mimics the Ca2+ dysregulation of aggregated AS. CPA reduces NF‐κB nuclear translocation in OLN cells and increases survival in neurons.
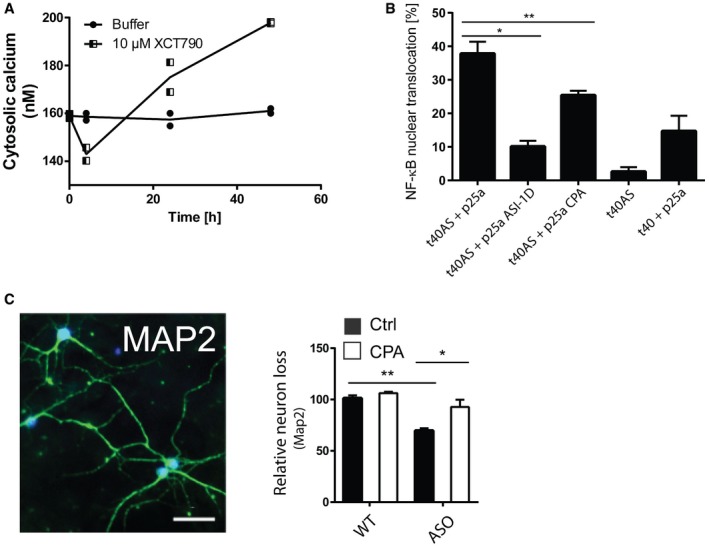
- Allosteric activation of SERCA by XCT790 mimics the early decrease and later increase in Ca2+ observed upon intracellular AS aggregation. Cytosolic Ca2+ levels were quantified by the Ca2+ sensor Fura‐2 and converted to absolute values using the Fura‐2 Calcium Imaging Calibration Kit. Non‐mitotic SH‐SY5Y wt cells were generated by treatment with 10 μM retinoic acid for 2 days before treatment with SERCA activator, 10 μM XCT790 (Sigma‐Aldrich). The cytosolic Ca2+ in SH‐SY5Y cells was measured after 4, 24 and 48 h. Points represent Ca2+ concentrations as mean ± SD, N = 2.
- CPA reduces NF‐κB nuclear translocation in OLN cells. Aggregation of AS in OLN cells by co‐expression of AS and p25a generates a cell stress that increases nuclear translocation of NF‐κB (p65), which can be rescued by ASI‐1D treatment 10. Bars represent the average percentage of transfected cells with NF‐κB translocated to the nucleus ± SD in > 100 transfected cells in each experiment (one‐way ANOVA multiple comparisons with Sidak post hoc test, *P = 0.0001 and **P = 0.0006). N = 3.
- Survival of neurons from day 6 to day 14 was quantified by counting MAP2‐positive cells. Representative MAP2 staining pattern (green) of primary hippocampal neurons with NeuN marking neuronal nuclei. Scale bar is 50 μm. Bars represent remaining MAP‐2‐positive neurons at day 14 normalised to the number present at day 6, presented as means of three individual experiments ± SD each of > 300 neurons (one‐way ANOVA multiple comparisons with Sidak post hoc test, *P = 0.0003, **P = 0.0001).
