Fig. 1.
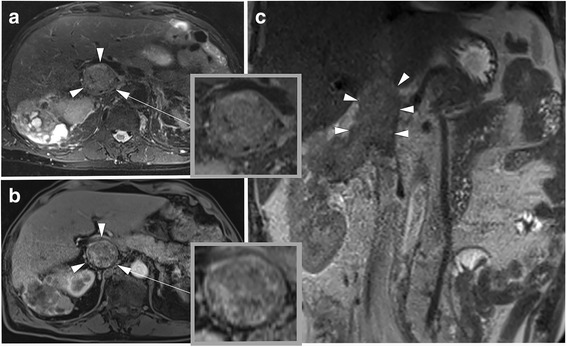
Images in a 55-year old man with a clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and an inferior vena cava (IVC) tumor thrombus with wall invasion. The RCC extends from the right kidney into the suprahepatic IVC. a axial fat-saturated T2-weighted image. b T1-weighted contrast-enhanced 3D GRE (VIBE) image (arterial phase) and (c), coronal T2-weighted HASTE image for anatomic reference. Note that the thrombus completely obstructs the lumen of the IVC and shows direct contact with the vessel wall (a, c). The contrast-enhanced image (b) demonstrates a heterogeneous enhancement of the tumor thrombus, and contact to, but no breach of the vessel wall, which makes IVC wall invasion likely. During extended nephrectomy, this thrombus was partly adherent the IVC and after extraction of the IVC thrombus, continuous suturing became necessary. VIBE = Volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination
