Fig. 1.
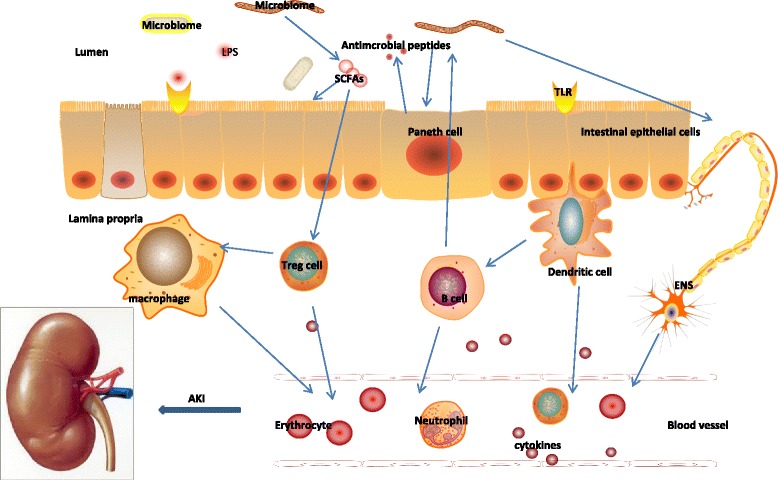
Effect of disruption of the gut mucosal barrier and bacterial translocation on the systemic inflammatory response in septic AKI. During sepsis, the combined effect of disruption of the mucus membrane barrier, a shift in the composition and virulence of intestinal microbes, and microbe translocation in gut lead to expansive inflammation, which will further alter host immune and metabolic homeostasis. The altered immune homeostasis and systemic inflammation can promote AKI in sepsis
