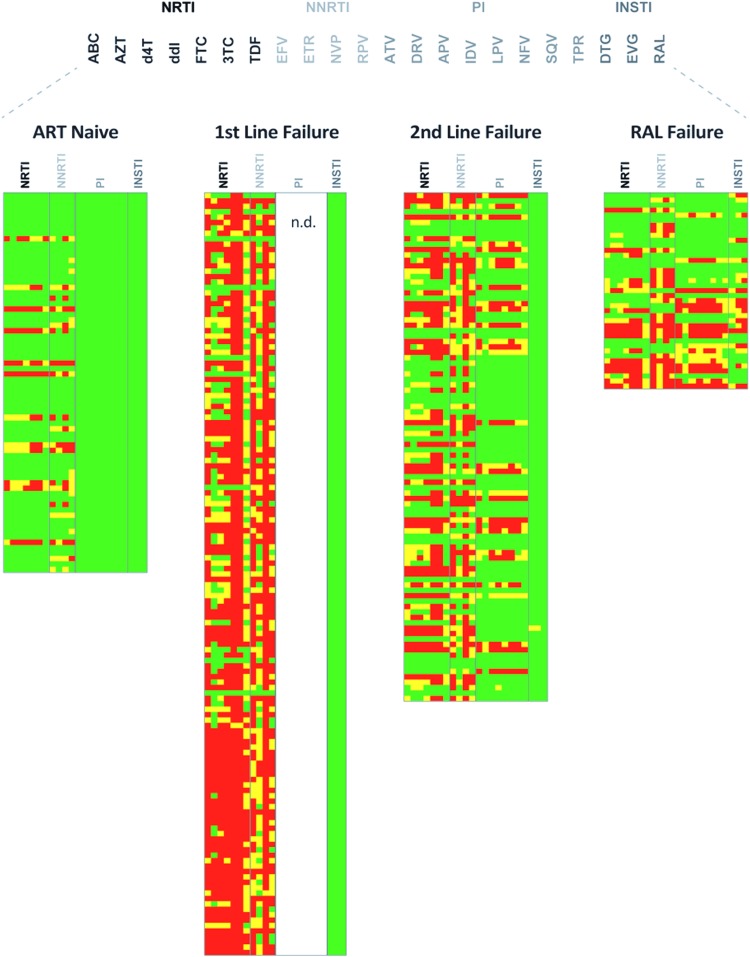
FIG. 4.
HIV-1 genotypic resistance interpretation based on Sanger sequencing. Amino acid substitutions was used with HIVdb program Genotypic resistance interpretation algorithm from Stanford university HIV drug resistance database (https://hivdb.stanford.edu) to predict the levels of susceptibility to PR, RT, and INSTIs. A susceptible genotype is shown in green, intermediate- and high-level resistance is shown in yellow and red, respectively. ABC, abacavir; AZT, zidovudine; D4T, stavudine; DDI, didanosine; FTC, emtricitabine; 3TC, lamivudine; TDF, tenofovir; EFV, efavirenz; ETR, etravirine; NVP, nevirapine; RPV, rilpivirine; ATVr, atazanavir/r; DRVr, darunavir/r; FPVr, fosamprenavir/r; IDVr, indinavir/r; LPVr, lopinavir/r; NFV, nelfinavir; SQVr, saquinavir/r TPVr, tipranavir/r; DTG, dolutegravir; EVG, elvitegravir. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/aid