Figure 10.
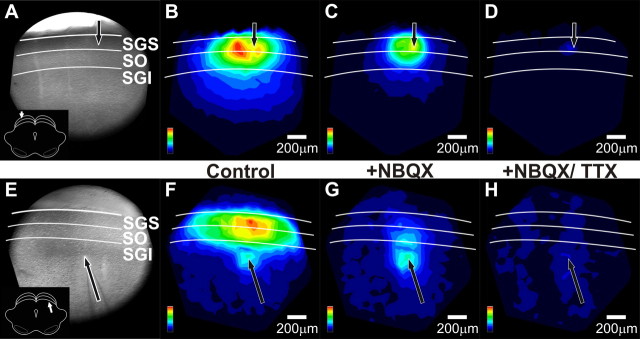
NBQX and TTX alter the spatial patterns of initial-spikes in SC. A, CCD image of the SC slice preparation. The arrow indicates the point of stimulation and the inset shows orientation of the coronal slice (cortex removed). White lines and labels denote the layers of the SC. B, Color map image of the initial-spike signal propagation following SGS stimulation before drug application, normalized to the maximum amplitude of the initial-spike (0–10 ms). Hotter colors indicate higher amplitude signals. Color scales are in the lower right corner of each panel. Layers of the SC are demarked as in A. Scale bars, 200 μm. C, Color map image of the initial-spike signal propagation following SGS stimulation after addition of 5 μm NBQX, normalized to the maximum amplitude of the initial-spike before drug application, i.e., the data shown in B. D, Color map image of the initial-spike signal propagation following SGS stimulation after addition of 5 μm NBQX plus 300 nm TTX. The normalization is the same as in B and C. E–H, Same as A–D, respectively, but for SGI stimulation. Note that cortex is not removed in the CCD image in E.